Breadcrumb
Maximizing the signal to leakage ratio in downlink cellular networks
A transmission scheme is developed for the downlink frame of cellular networks. While the mobile stations (MSs) maximize the signal power from the serving base station (BS), each BS aims at balancing the signal power of its users with the interference caused at the MSs of the neighboring cells, based on an approximated performance metric. A closed form solution for the beamforming vectors of the BSs and the MSs is derived. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme achieves substantial gains for different antenna configurations, outperforming well-known schemes in the literature. © 2013
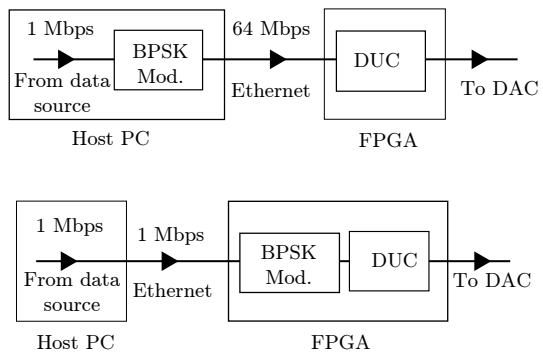
Maximizing USRP N210 SDR transfer rate by offloading modulation to the on-board FPGA
One of the challenges of the design of Software Defined Radios (SDR) is to maintain a high level of reconfigurability without sacrificing data rates. In this paper, we consider the USRP N210, which is an SDR kit made by Ettus Research. It consists of an FPGA connected to an RF front-end. The USRP is operated by a host computer where most of the processing is done while the FPGA is used mainly to control the RF front-end, manage communication with the host, and convert sample rates. The maximal rate supported by the USRP hardware can not be practically achieved due to the bottleneck in the data
Synthetic generation of radio maps for device-free passive localization
In this paper, we present the design, implementation, and evaluation of a system that automatically constructs accurate radio maps for device-free WLAN localization systems. The system is capable of generating deterministic and probabilistic radio maps for localization systems. Our system uses 3D ray tracing enhanced with the uniform theory of diffraction (UTD) to model the electric field behavior and the human shadowing effect. We present our system architecture and describe the details of its different components. We also propose an optional module, location-0 correction, that can
Hidden anchor: Providing physical layer location privacy in hybrid wireless sensor networks
In many hybrid wireless sensor networks (HWSNs) applications, sensor nodes are deployed in hostile environments where trusted and un-trusted nodes co-exist. In such hybrid networks, it becomes important to allow trusted nodes to share information, especially, location information and, at the same time, prevent un-trusted nodes from gaining access to this information. We focus on anchor-based localization algorithms in HWSNs, where a small set of specialized nodes, i.e. anchor nodes, broadcast their location to the network and other nodes can use the broadcast information to estimate their own
Collision Probability Computation for Road Intersections Based on Vehicle to Infrastructure Communication
In recent years, many probability models proposed to calculate the collision probability for each vehicle and those models used in collision avoidance algorithms and intersection management algorithms. In this paper, we introduce a method to calculate the collision probability of vehicles at an urban intersection. The proposed model uses the current position, speed, acceleration, and turning direction then each vehicle shares its required information to the roadside unit (RSU) via the Vehicle to Infrastructures (V2I). RSU can predict each vehicle's path in intersections by using the received
Optimum Scheduling the Electric Distribution Substations with a Case Study: An Integer Gaining-Sharing Knowledge-Based Metaheuristic Algorithm
This work is dedicated to the economic scheduling of the required electric stations in the upcoming 10-year long-term plan. The calculation of the required electric stations is carried out by estimating the yearly consumption of electricity over a long-time plan and then determining the required number of stations. The aim is to minimize the total establishing and operating costs of the stations based on a mathematical programming model with nonlinear objective function and integer decision variables. The introduced model is applied for a real practical case study to conclude the number of
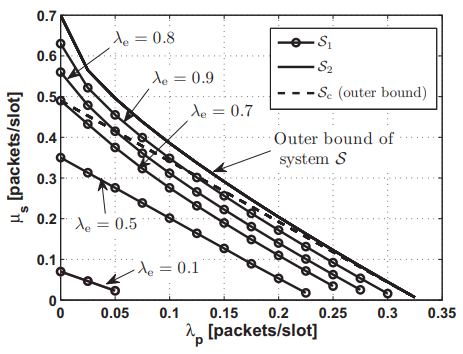
Maximum throughput of a cooperative energy harvesting cognitive radio user
In this paper, we investigate the maximum throughput of a saturated rechargeable secondary user (SU) sharing the spectrum with a primary user (PU). The SU harvests energy packets (tokens) from the environment with a certain harvesting rate. All transmitters are assumed to have data buffers. In addition to its own traffic buffer, the SU has a buffer for storing the admitted primary packets for relaying; and a buffer for storing the energy tokens harvested from the environment. We propose a new cooperative cognitive relaying protocol that allows the SU to relay a fraction of the undelivered
Differential Evolution Mutations: Taxonomy, Comparison and Convergence Analysis
During last two decades, Differential Evolution (DE) proved to be one of the most popular and successful evolutionary algorithms for solving global optimization problems over continuous space. Proposing new mutation strategies to improve the optimization performance of (DE) is considered a significant research study. In DE, mutation operation plays a vital role in the performance of the algorithm. Therefore, in this paper, comprehensive analysis of the contributions on basic and novel mutation strategies that were proposed between 1995 and 2020 is presented. A new taxonomy based on the
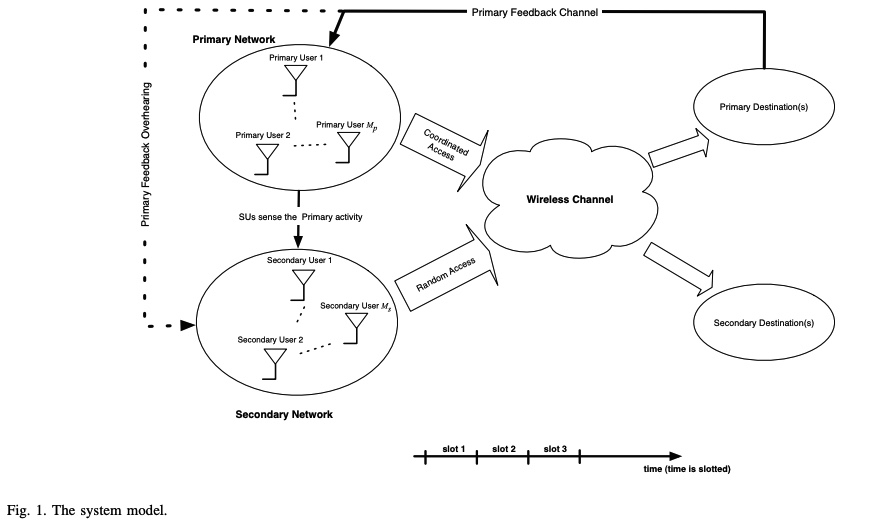
A feedback-soft sensing-based access scheme for cognitive radio networks
In this paper, we examine a cognitive spectrum access scheme in which secondary users exploit the primary feedback information. We consider an overlay secondary network employing a random access scheme in which secondary users access the channel by certain access probabilities that are functions of the spectrum sensing metric. In setting our problem, we assume that secondary users can eavesdrop on the primary link's feedback. We study the cognitive radio network from a queuing theory point of view. Access probabilities are determined by solving a secondary throughput maximization problem
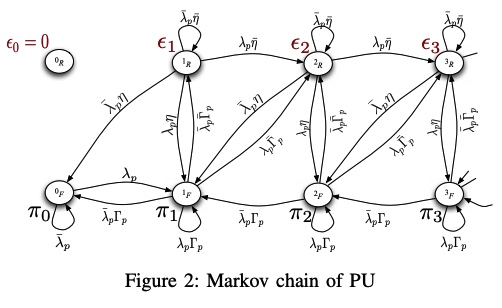
A feedback-based access scheme for cognitive-relaying networks
In this paper, we consider a cognitive relaying network in which the secondary user accesses the channel with a certain access probability that depends on the feedback information sent by the primary destination. In addition, the secondary user is granted relaying capabilities by which it can relay primary traffic that was unsuccessfully transmitted by the primary user. We show that this proposed scheme enhances the performance of the secondary user as well as the primary user, while the QoS requirements of the primary user is unviolated. The secondary user can avoid sure collisions with the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 9
- Next page ››
