Breadcrumb
A new method for parameter extraction of solar photovoltaic models using gaining–sharing knowledge based algorithm
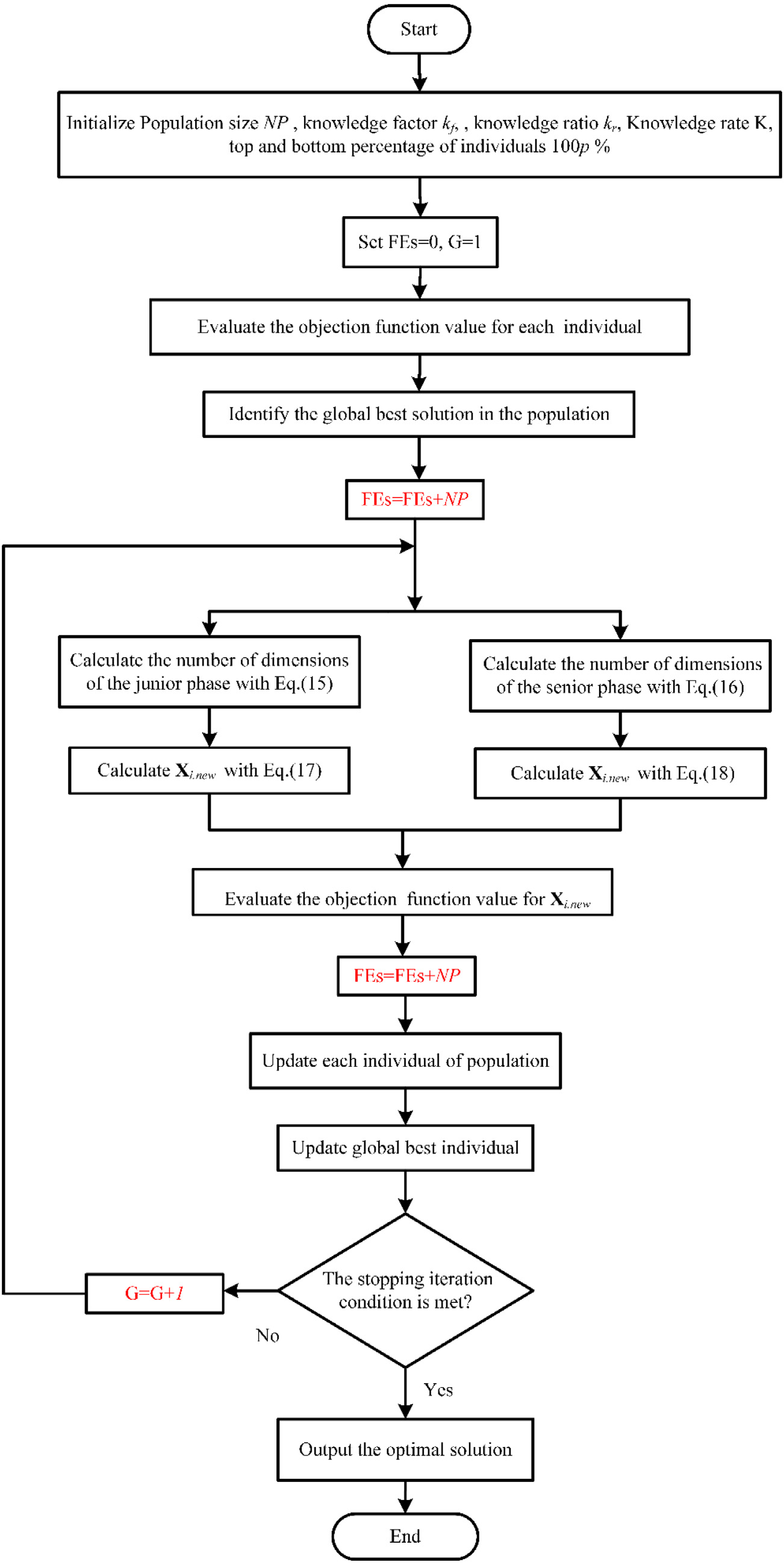
For the solar photovoltaic (PV) system to operate efficiently, it is necessary to effectively establish an equivalent model of PV cell and extract the relevant unknown model parameters accurately. This paper introduces a new metaheuristic algorithm, i.e., gaining-sharing knowledge based algorithm (GSK) to solve the solar PV model parameter extraction problem. This algorithm simulates the process of knowledge acquisition and sharing in the human life cycle and is with strong competitiveness in solving optimization problems. It includes two significant phases. The first phase is the beginner
A novel stochastic geometrical model for wideband MIMO-V2V channels
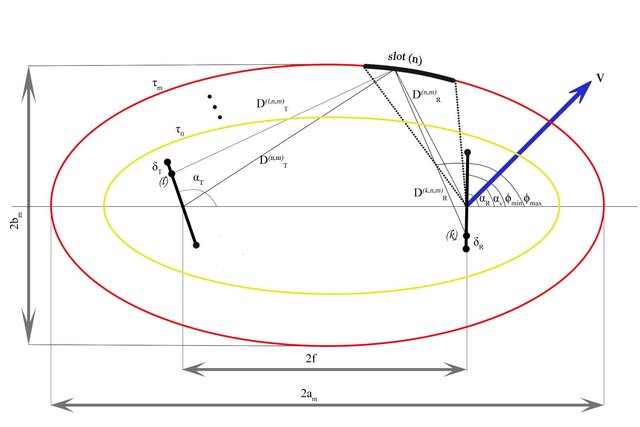
In this paper, we present a novel wideband multiple-input multiple-output Vehicle-to-Vehicle channel model. The proposed channel model is derived using the geometrical elliptical scattering approach. In order to emulate the appearance and disappearance of scatterers (vehicles, terrain, roadside units, etc.) in the environment, we associate a persistence process with each physical scatterer in the model. The parameters of the proposed model can be tuned to represent a variety of vehicular environments. We also derive the temporal and spatial correlation functions of the channel coefficients
A Neural Network-Based VLC Indoor Positioning System for Moving Users
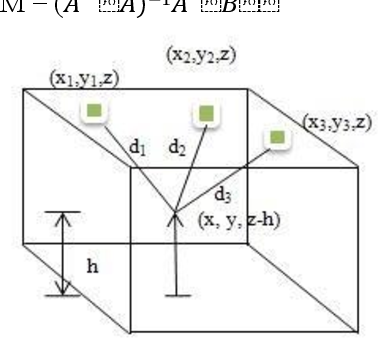
In this paper, we present an indoor visible light communication (VLC) system to estimate the position of a moving user. This system uses two approaches based on received signal strength, trilateration estimation, and neural network estimation. In the VLC system, each transmitter sends its position information via light. A photo-detector receiver supported with the moving user is used to receive the transmitted power from each transmitter. The receiver position is calculated using the estimation of trilateration and the prediction of the neural network. We consider the sight line (LOS) and non
Stability Analysis of Slotted Aloha with Opportunistic RF Energy Harvesting
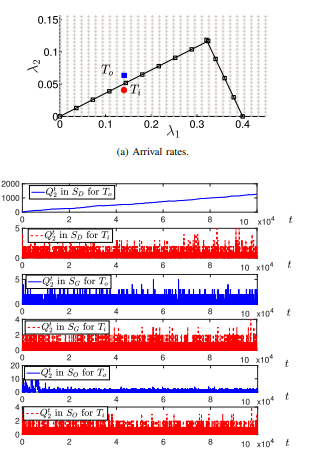
Energy harvesting (EH) is a promising technology for realizing energy-efficient wireless networks. In this paper, we utilize the ambient RF energy, particularly interference from neighboring transmissions, to replenish the batteries of the EH enabled nodes. However, RF energy harvesting imposes new challenges into the analysis of wireless networks. Our objective in this paper is to investigate the performance of a slotted Aloha random access wireless network consisting of two types of nodes, namely Type I, which has unlimited energy supply and Type II, which is solely powered by an RF energy
Real-Time Geometric Representation of Lane-Change Decision for Autonomous Vehicles Using Dynamic Optimization Algorithm
This paper develops a lane-change geometric representation that can be used in an on-road vehicle. The design of the proposed system uses the data collected from active a host vehicle and measures the relative speed between host vehicle and obstacle vehicles in real-time. The available distance to the target lanes measures the separated distance between the host and obstacle vehicles in real-time. These data are generated automatically using a dynamic environment and updated using time and object dynamics laws. The main algorithm uses the data to test the availability of using lane-change
Coded Caching and Spatial Multiplexing Gains in MIMO Interference Networks
This paper studies the Multi-Input-Multi-Output (MIMO) interference networks with arbitrary number of transmitters and receivers, where both the transmitters and receivers are equipped with caches. Our objective is to propose content placement and delivery schemes that minimize the worst case normalized delivery time (NDT). First, we design a delivery scheme for the cache-aided Single-Input-Multiple-Output (SIMO) interference networks. Then, we obtain the achievable NDT of the cache-aided MIMO interference networks by using the decomposition property. The numerical results show the superiority
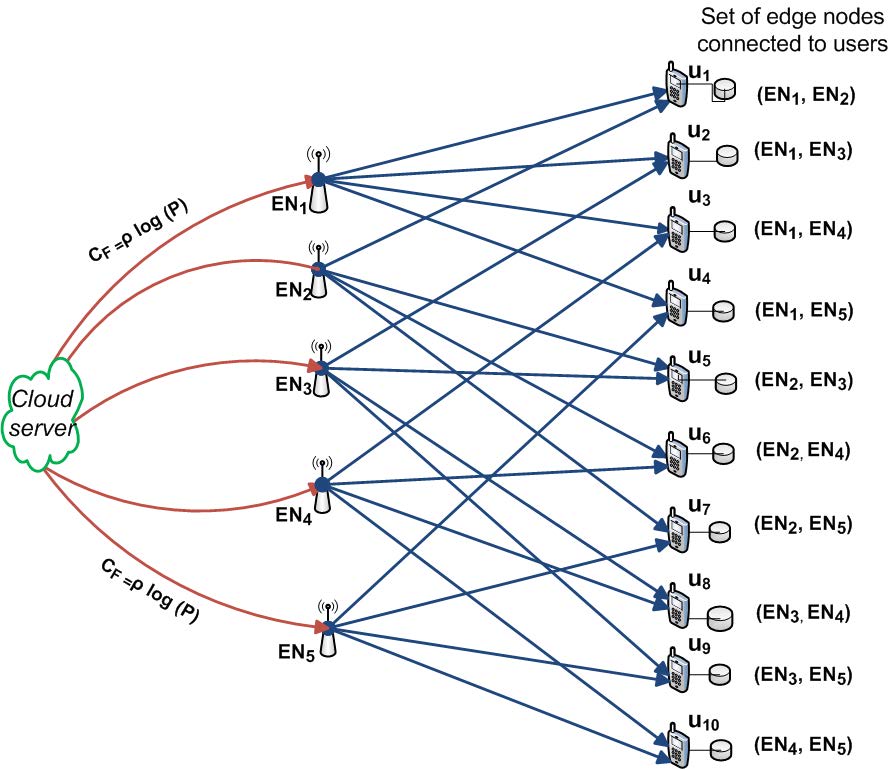
Cache-aided fog radio access networks with partial connectivity
Centralized coded caching and delivery is studied for a partially-connected fog radio access network (F-RAN), whereby a set of H edge nodes (ENs) (without caches), connected to a cloud server via orthogonal fronthaul links, serve K users over the wireless edge. The cloud server is assumed to hold a library of N files, each of size F bits; and each user, equipped with a cache of size MF bits, is connected to a distinct set of r ENs; or equivalently, the wireless edge from the ENs to the users is modeled as a partial interference channel. The objective is to minimize the normalized delivery time
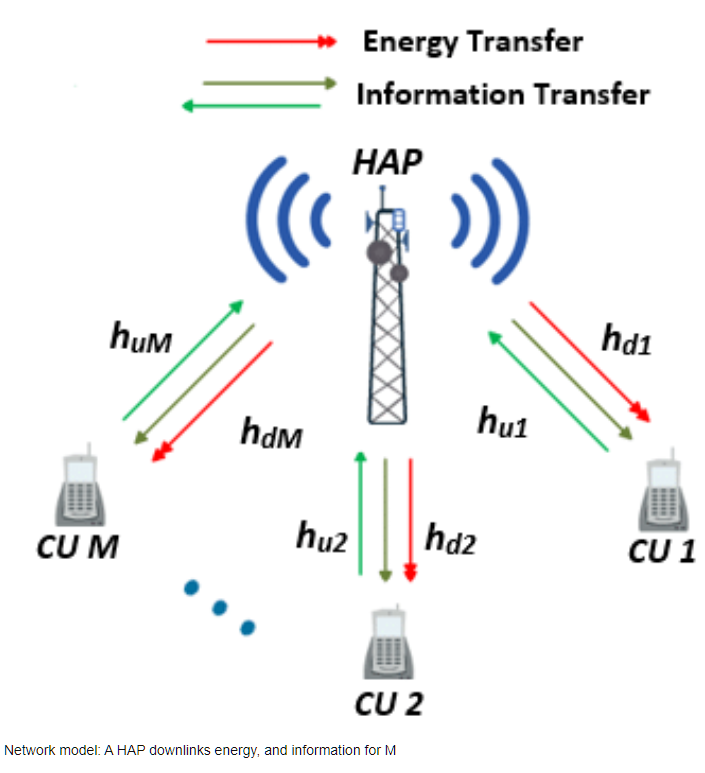
Optimal uplink and downlink resource allocation for wireless powered cellular networks
In this paper, we characterize optimal resource allocation for the uplink and downlink of wireless powered cellular networks (WPCNs). In particular, we investigate a time-slotted WPCN, where a hybrid access point (HAP) is in charge of energy replenishing of M cellular users (CUs), along with transmission/reception of information to/from them. Unlike prior works, which give attention to information transmission in only one direction (either uplink or downlink), our work incorporates information transmission in both directions, along with energy transfer over the downlink. Besides harvesting
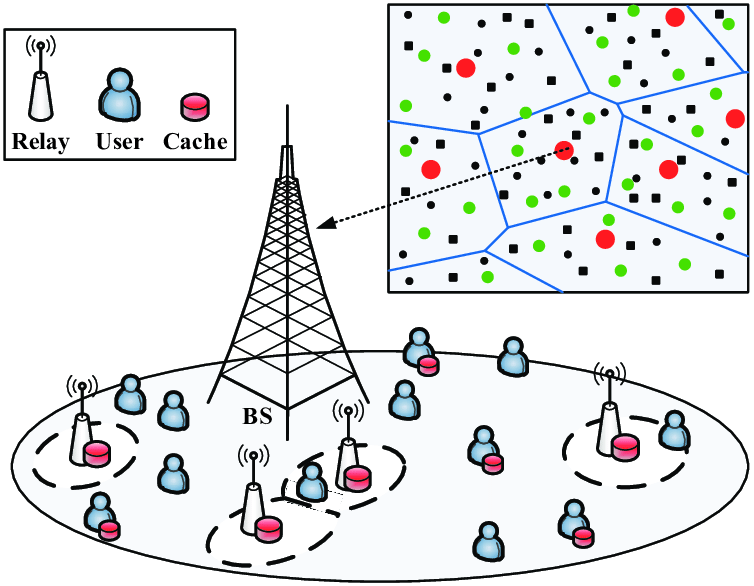
Cache-aided heterogeneous networks: Coverage and delay analysis
This paper characterizes the performance of a generic K-tier cache-aided heterogeneous network (CHN), in which the base stations (BSS) across tiers differ in terms of their spatial densities, transmission powers, pathloss exponents, activity probabilities conditioned on the serving link and placement caching strategies. We consider that each user connects to the BS which maximizes its average received power and at the same time caches its file of interest. Modeling the locations of the BSS across different tiers as independent homogeneous Poisson Point processes (HPPPs), we derive closed-form
Novel cooperative policy for cognitive radio networks: Stability region and delay analysis
We consider a cognitive radio system that consists of primary user, secondary user, and their destinations. The secondary user has a relaying capability, i.e., it transmits the relayed packets from the primary user. Unlike most of the previous works that restrict the secondary user to transmit only in the idle time slots, we assume that the secondary user interferes on the primary user with certain probability that is optimized to maximize the stable throughput of the secondary network under certain level of quality of service constraints for the primary one. We show how significantly our
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 20
- Next page ››
