Breadcrumb
Real-Time Geometric Representation of Lane-Change Decision for Autonomous Vehicles Using Dynamic Optimization Algorithm
This paper develops a lane-change geometric representation that can be used in an on-road vehicle. The design of the proposed system uses the data collected from active a host vehicle and measures the relative speed between host vehicle and obstacle vehicles in real-time. The available distance to the target lanes measures the separated distance between the host and obstacle vehicles in real-time. These data are generated automatically using a dynamic environment and updated using time and object dynamics laws. The main algorithm uses the data to test the availability of using lane-change
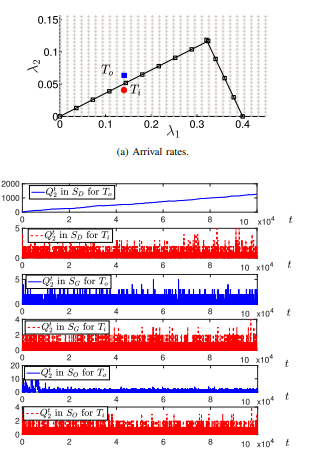
Stability Analysis of Slotted Aloha with Opportunistic RF Energy Harvesting
Energy harvesting (EH) is a promising technology for realizing energy-efficient wireless networks. In this paper, we utilize the ambient RF energy, particularly interference from neighboring transmissions, to replenish the batteries of the EH enabled nodes. However, RF energy harvesting imposes new challenges into the analysis of wireless networks. Our objective in this paper is to investigate the performance of a slotted Aloha random access wireless network consisting of two types of nodes, namely Type I, which has unlimited energy supply and Type II, which is solely powered by an RF energy
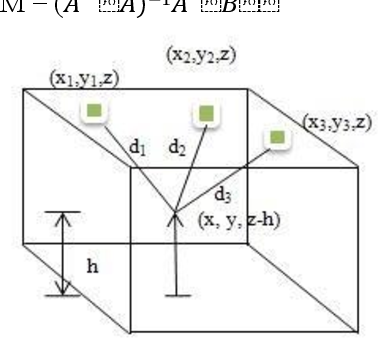
A Neural Network-Based VLC Indoor Positioning System for Moving Users
In this paper, we present an indoor visible light communication (VLC) system to estimate the position of a moving user. This system uses two approaches based on received signal strength, trilateration estimation, and neural network estimation. In the VLC system, each transmitter sends its position information via light. A photo-detector receiver supported with the moving user is used to receive the transmitted power from each transmitter. The receiver position is calculated using the estimation of trilateration and the prediction of the neural network. We consider the sight line (LOS) and non
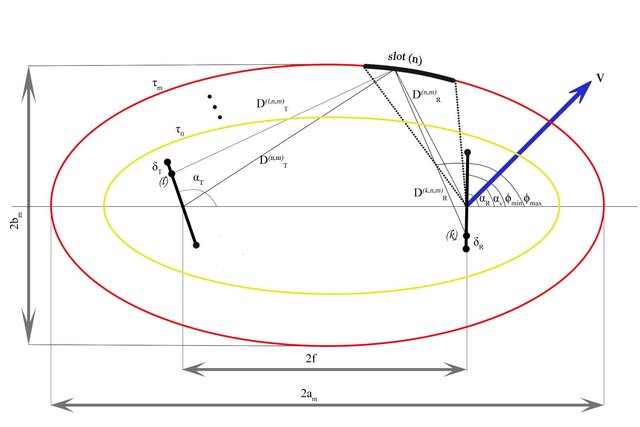
A novel stochastic geometrical model for wideband MIMO-V2V channels
In this paper, we present a novel wideband multiple-input multiple-output Vehicle-to-Vehicle channel model. The proposed channel model is derived using the geometrical elliptical scattering approach. In order to emulate the appearance and disappearance of scatterers (vehicles, terrain, roadside units, etc.) in the environment, we associate a persistence process with each physical scatterer in the model. The parameters of the proposed model can be tuned to represent a variety of vehicular environments. We also derive the temporal and spatial correlation functions of the channel coefficients
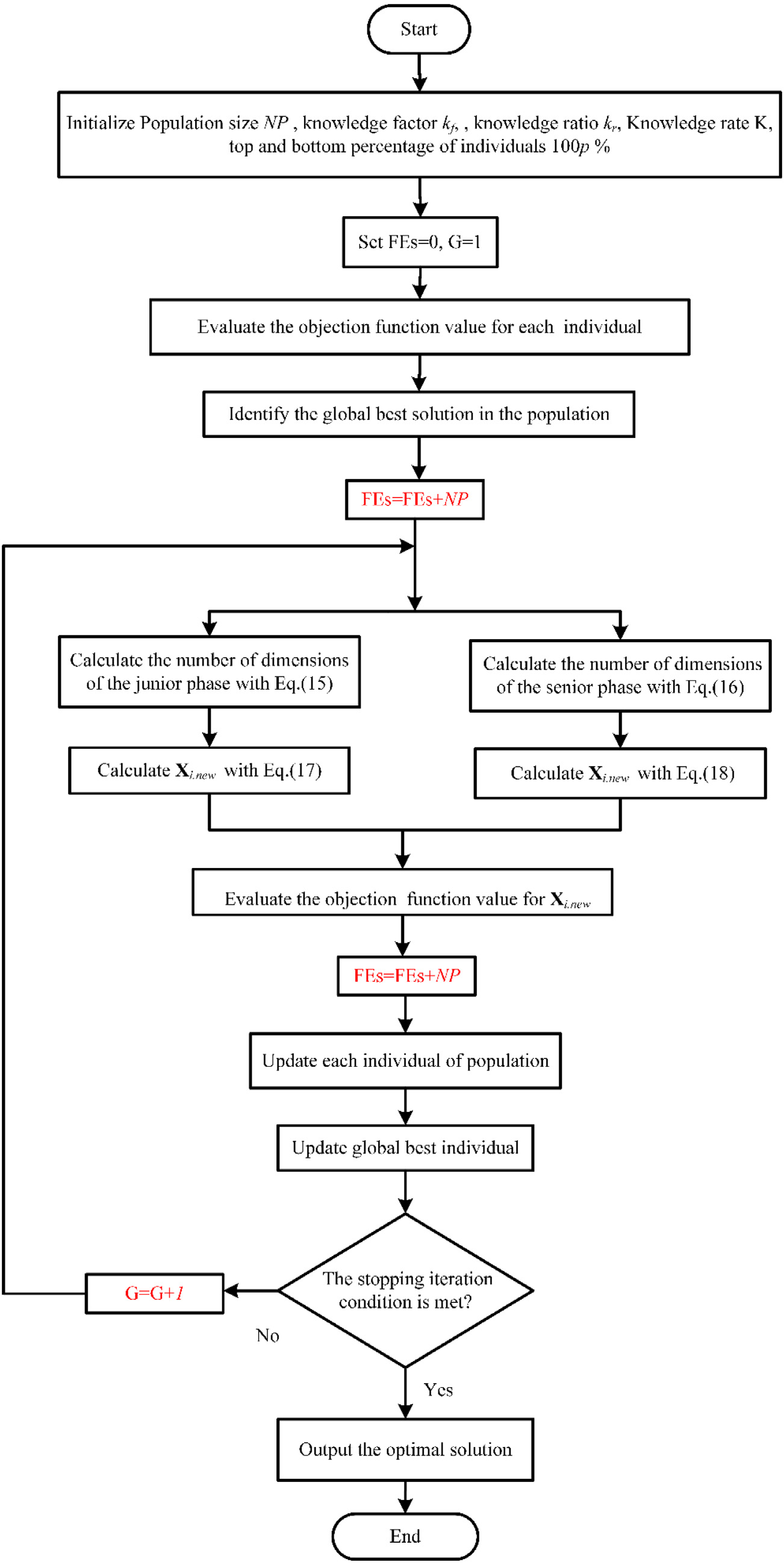
A new method for parameter extraction of solar photovoltaic models using gaining–sharing knowledge based algorithm
For the solar photovoltaic (PV) system to operate efficiently, it is necessary to effectively establish an equivalent model of PV cell and extract the relevant unknown model parameters accurately. This paper introduces a new metaheuristic algorithm, i.e., gaining-sharing knowledge based algorithm (GSK) to solve the solar PV model parameter extraction problem. This algorithm simulates the process of knowledge acquisition and sharing in the human life cycle and is with strong competitiveness in solving optimization problems. It includes two significant phases. The first phase is the beginner
Solution of Uncertain Solid Transportation Problem by Integer Gaining Sharing Knowledge Based Optimization Algorithm
This paper presents the application of gaining sharing knowledge (GSK) based optimization algorithm to an uncertain solid transportation (UST) problem. The UST problem consists of supply, demand, and conveyance constraints under uncertain environment. To solve the said problem, the expected criterion model is considered so that the expected value of the objective function is minimized. 99-method generates the expected value of the assumed uncertain variables, and the transformed problem is solved. Due to the consideration of integer decision variables, GSK is modified to integer gaining
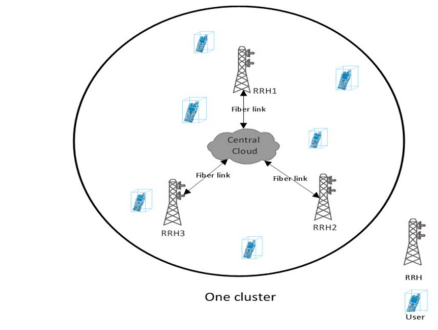
Energy Efficiency Optimization through RRHs ON/OFF Switching Technique in C-RAN
Energy efficiency (EE) is one of the main parameters to be considered in recent networks targeting green technology. Our system is based on cloud radio access networks and it consists of a macro base-station and many small remote radio heads (RRHs). We solve an optimization problem to improve the system's EE through resource allocation and power control. We also reduce the power consumption through switching the RRHs ON/OFF based on the current users' distribution. We formulate the problem as EE maximization with constraints to provide full frequency reuse between RRHs. Our solution divides
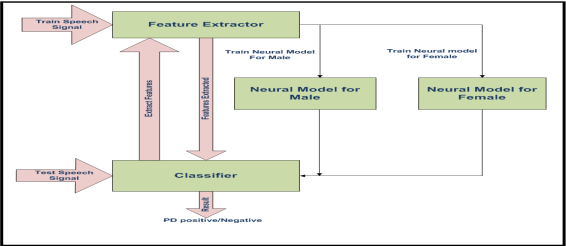
Enhancing Parkinson's disease diagnosis accuracy through speech signal algorithm modeling
Parkinson's disease (PD), one of whose symptoms is dysphonia, is a prevalent neurodegenerative disease. The use of outdated diagnosis techniques, which yield inaccurate and unreliable results, continues to represent an obstacle in early-stage detection and diagnosis for clinical professionals in the medical field. To solve this issue, the study proposes using machine learning and deep learning models to analyze processed speech signals of patients' voice recordings. Datasets of these processed speech signals were obtained and experimented on by random forest and logistic regression classifiers
Proactive location-based scheduling of delay-constrained traffic over fading channels
In this paper, proactive resource allocation based on user location for point-to-point communication over fading channels is introduced, whereby the source must transmit a packet when the user requests it within a deadline of a single time slot. We introduce a prediction model in which the source predicts the request arrival Tp slots ahead, where Tp denotes the prediction window (PW) size. The source allocates energy to transmit some bits proactively for each time slot of the PW with the objective of reducing the transmission energy over the non-predictive case. The requests are predicted

Cooperative Q-learning techniques for distributed online power allocation in femtocell networks
In this paper, we address the problem of distributed interference management of femtocells that share the same frequency band with macrocells using distributed multi-agent Q-learning. We formulate and solve two problems representing two different Q-learning algorithms, namely, femto-based distributed and sub-carrier-based distributed power controls using Q-learning (FBDPC-Q and SBDPC-Q). FBDPC-Q is a multi-agent algorithm that works on a global basis, for example, deals with the aggregate macrocell and femtocell capacities. Its complexity increases exponentially with the number of sub-carriers
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 21
- Next page ››
