Breadcrumb
Proactive resource allocation in cognitive networks
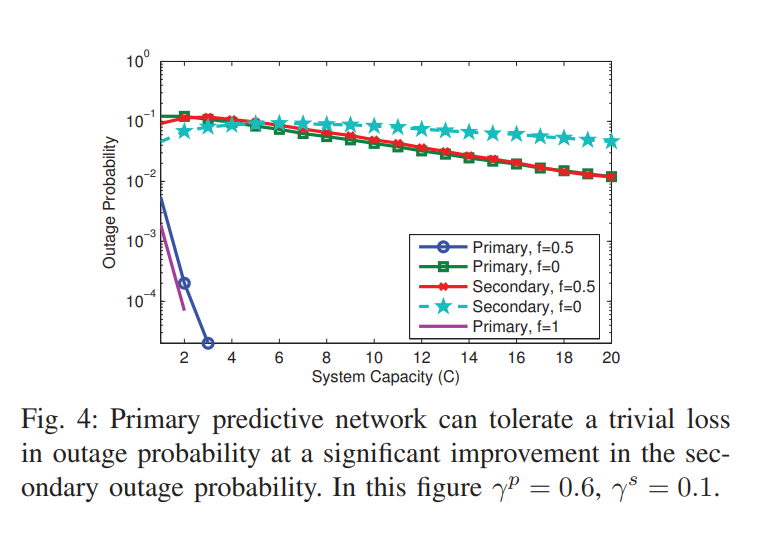
Recently we have introduced the notion of proactive resource allocation and predictive wireless networks, where intelligent wireless networks are capable of tracking and exploiting the repetition patterns in human behavior while accessing the network resources. This predictability advantage grants the network more flexibility to schedule users' requests over a longer time horizon, and thereby significantly improves the quality of service (QoS) defined as outage probability. In this paper we extend our analysis to consider a network of two different QoS classes. The first is a primary class
QOS-constrained multiuser peer-to-peer amplify-and-forward relay beamforming
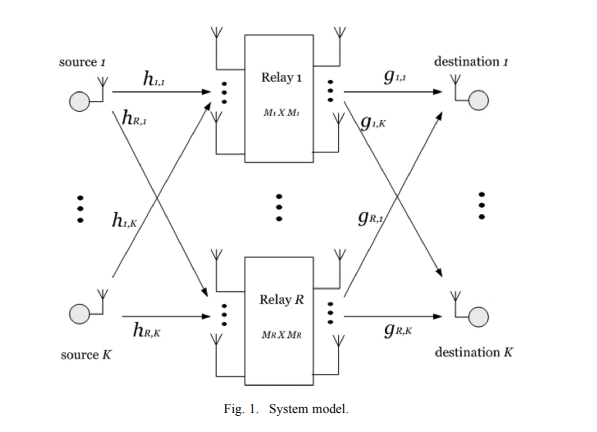
A wireless communication scenario is considered with K single-antenna source-destination pairs communicating through several half-duplex amplify-and-forward MIMO relays where each source is targeting only one destination. The relay beamforming matrices are designed in order to minimize the total power transmitted from the relays subject to quality of service constraints on the received signal to interference-plus-noise ratio at each destination node. Due to the nonconvexity of this problem, several approximations have been used in the literature to find a computationally efficient solution. A
Distributed spectrum sensing with sequential ordered transmissions to a cognitive fusion center
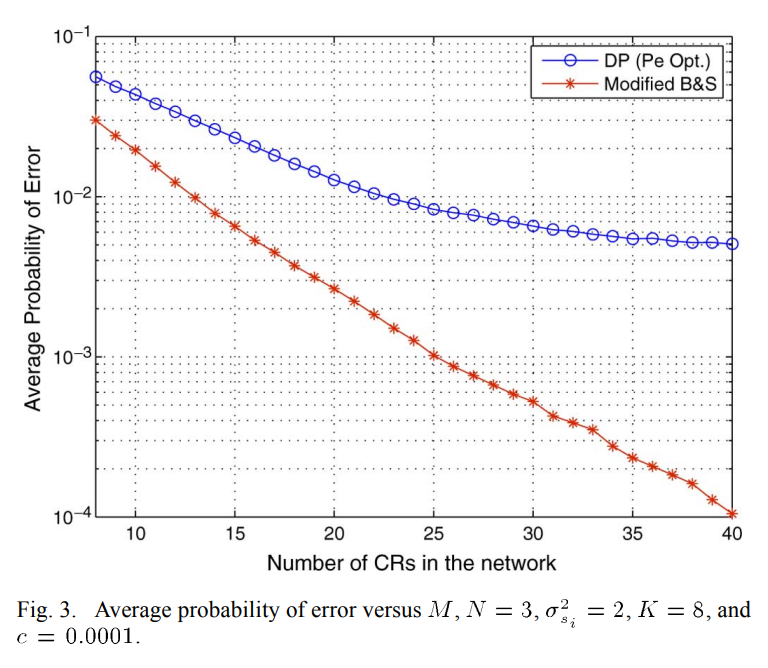
Cooperative spectrum sensing is a robust strategy that enhances the detection probability of primary licensed users. However, a large number of detectors reporting to a fusion center for a final decision causes significant delay and also presumes the availability of unreasonable communication resources at the disposal of a network searching for spectral opportunities. In this paper, we employ the idea of sequential detection to obtain a quick, yet reliable, decision regarding primary activity. Local detectors take measurements, and only a few of them transmit the log likelihood ratios (LLR) to

Degrees of freedom in cached MIMO relay networks with multiple base stations
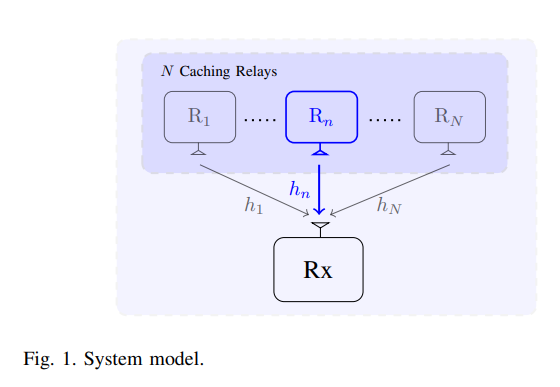
The ability of physical layer relay caching to increase the degrees of freedom (DoF) of a single cell was recently illustrated. In this paper, we extend this result to the case of multiple cells in which a caching relay is shared among multiple non-cooperative base stations (BSs). In particular, we show that a large DoF gain can be achieved by exploiting the benefits of having a shared relay that cooperates with the BSs. We first propose a cache-assisted relaying protocol that improves the cooperation opportunity between the BSs and the relay. Next, we consider the cache content placement
On Caching and Base Station Densification Tradeoff for Maximized Energy Efficiency
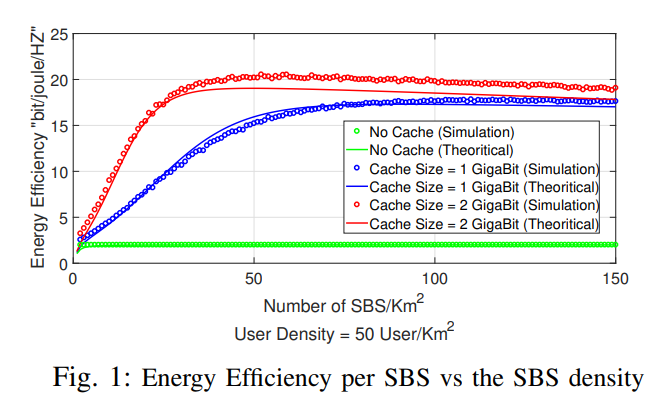
In this paper, we study a two-tier cellular network with cache-enabled small base stations (SBSs). In our model, a SBS has the ability to coordinate with neighboring SBSs and fetch data from their caches. We focus on the effect of SBSs' density on the network's energy efficiency. To this end, stochastic geometry theory is used to model the SBSs and users distributions, which enables us to find closed-form expressions for the network's energy efficiency as a function of the SBSs density and the cache size at each SBS. The optimal SBSs density that maximizes the energy efficiency is
Proactive power allocation and caching node selection for regular service guarantees
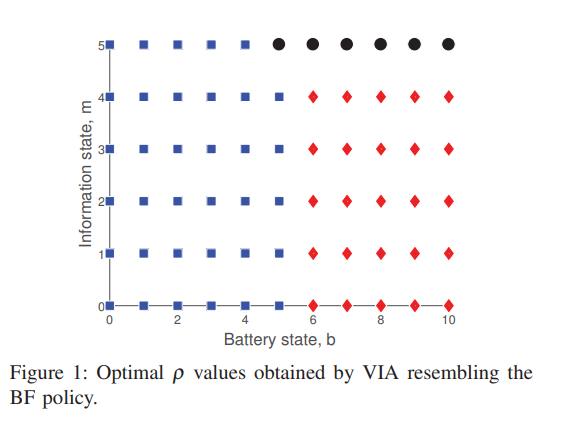
This paper studies the potential of proactive resource allocation to prolong the communication sessions in networks with limited energy budgets and stringent quality-of-service (QoS) requirement, particularly a regular service guarantee. A threshold-based proactive communication policy is proposed to minimize the consumed transmission energy and maximize the network lifetime based on the different link states and the buffer state at the destination node. A closed-form expression is presented for the proactive gain in terms of the channel gain threshold, the amount of the proactively-
Wireless energy and information transfer in networks with hybrid ARQ
In this paper, we consider a class of wireless powered communication devices using hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) protocol to ensure reliable communications. In particular, we analyze the trade-off between accumulating mutual information and harvesting RF energy at the receiver of a point-to-point link over a time-varying independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) channel. The transmitter is assumed to have a constant energy source while the receiver relies, solely, on the RF energy harvested from the received signal. At each time slot, the incoming RF signal is split between
Degrees of Freedom of the Full-Duplex Asymmetric MIMO Three-Way Channel with Unicast and Broadcast Messages
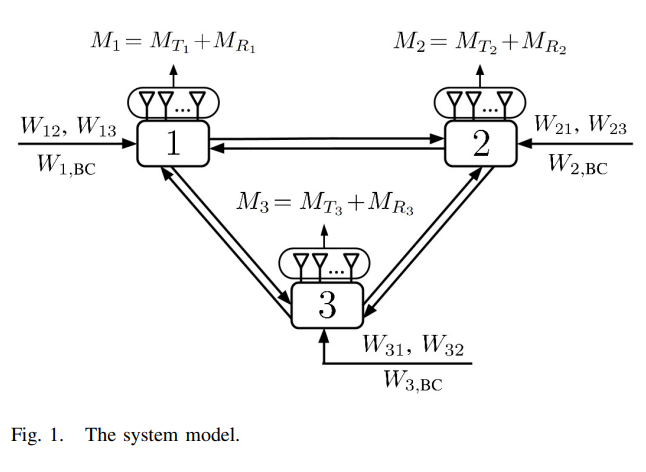
In this paper, we characterize the total degrees of freedom (DoFs) of the full-duplex asymmetric multiple-input multiple- output (MIMO) three-way channel. Each node has a separate-antenna full-duplex MIMO transceiver with a different number of antennas, where each antenna can be configured for either signal transmission or reception. We study this system under two message configurations; the first configuration is when each node has two unicast messages to be delivered to the two other nodes, while the second configuration is when each node has two unicast messages as well as one broadcast

LTE dynamic scheduling scheme for massive M2M and H2H communication
Machine-to-Machine (M2M) has become a generally used term owing to the concept of the Internet of Things (IOT). M2M communications have numerous areas of implementation such as medicine, transportation, environmental monitoring, and smart grids. As the field of its implementation extends, the number of M2M equipment are projected to grow proportionally in the upcoming few years. Current cellular network technologies will not be able to cope with the expected increase in the number of M2M services while considering QoS as a major topic. Many applications of M2M are delay sensitive that will

Weighted sum degrees of freedom of the asymmetric MIMO y channel with common and private messages
This paper investigates the weighted sum degrees of freedom (DoF) of the MIMO Y channel that consists of three users, where the j-Th user is equipped with Mj antennas, and a relay equipped with N antennas. In this network, each user conveys two private messages to the other two users in addition to a common message directed to both of them. As there is no direct link between the users, communication occurs through the relay. We define a weighted sum DoF metric that integrates all the network messages and weights the common message by a factor of α. Then, we study the weighted sum DoF
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 15
- Next page ››
