Breadcrumb
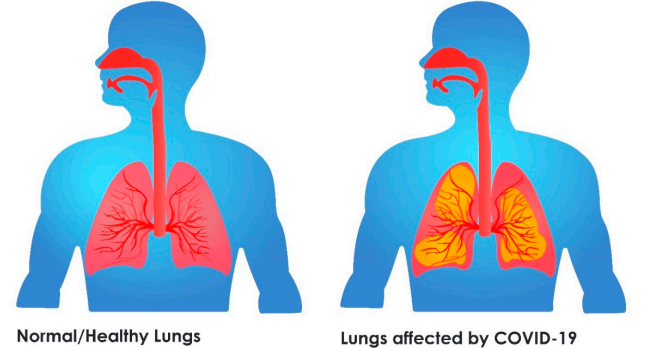
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis of Covid-19 Using CT-Scan
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) have been broadly used in our daily lives in different ways. Early detection of COVID-19 built on chest Computerized tomography CT empowers suitable management of patients and helps control the spread of the disease. We projected an artificial intelligence (AI) system for rapid COVID-19 detection using analysis of CTs of COVID-19 depending on the AI system. We developed and evaluated our system on a large dataset with more than 3000 CT volumes from COVID-19, viral community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and non-pneumonia subjects—1601 positive cases

Chaos-Based RNG using Semiconductor Lasers with Parameters Variation Tolerance
Random numbers play an essential role in guaranteeing secrecy in most cryptographic systems. A chaotic optical signal is exploited to achieve high-speed random numbers. It could be generated by using one or more semiconductor lasers with external optical feedback. However, this system faces two major issues, high peak to average power ratio (PAPR) and parameter variations. These issues highly affected the randomness of the generated bitstreams. In this paper, we use a non-linear compression technique to compand the generated signal before it is quantized to avoid the effects of the PAPR. Also
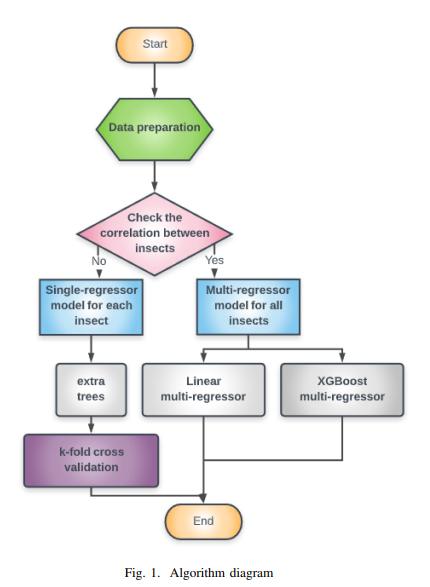
Guava Trees Disease Monitoring Using the Integration of Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics
The increase in population, food demand, and the pollution levels of the environment are considered major problems of this era. For these reasons, the traditional ways of farming are no longer suitable for early and accurate detection of biotic stress. Recently, precision agriculture has been extensively used as a potential solution for the aforementioned problems using high resolution optical sensors and data analysis methods that are able to cope with the resolution, size and complexity of the signals from these sensors. In this paper, several methods of machine learning have been utilized
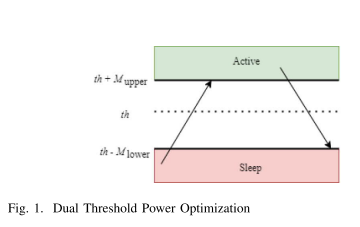
Optimal Power Consumption on Distributed Edge Services Under Non-Uniform Traffic with Dual Threshold Sleep/Active Control
Mobile edge computing (MEC) is a key enabling technology for supporting high-speed and low latency services in the fifth generation (5G) and beyond networks. MEC paradigm moves computational resources from centralized cloud servers towards the edge of the network, nearer to the users. However, edge computation resources increase the power consumption of the network. Moreover, the non-uniform traffic load on the edge servers causes resources to be underutilized and decrease the system's power efficiency. To achieve the green networking concept encouraged in 5G and beyond networks, unused MEC
Hybrid NOMA-based ACO-FBMC/OQAM for next-generation indoor optical wireless communications using LiFi technology
Light fidelity (LiFi) has successfully achieved high data transfer rates, high security, great availability, and low interference. In this paper, we propose a LiFi system consisting of a combination of non-orthogonal multi-access (NOMA), asymmetrically-clipped optical (ACO), and filter bank multicarrier (FBMC) techniques combined with offset quadrature amplitude modulation (OQAM). The paper also applies a μ-law companding approach for a high peak to average power ratio (PAPR) reduction of the FBMC/OQAM scheme. The combination of NOMA, ACO-FBMC/OQAM, and μ-law companding allows a significant
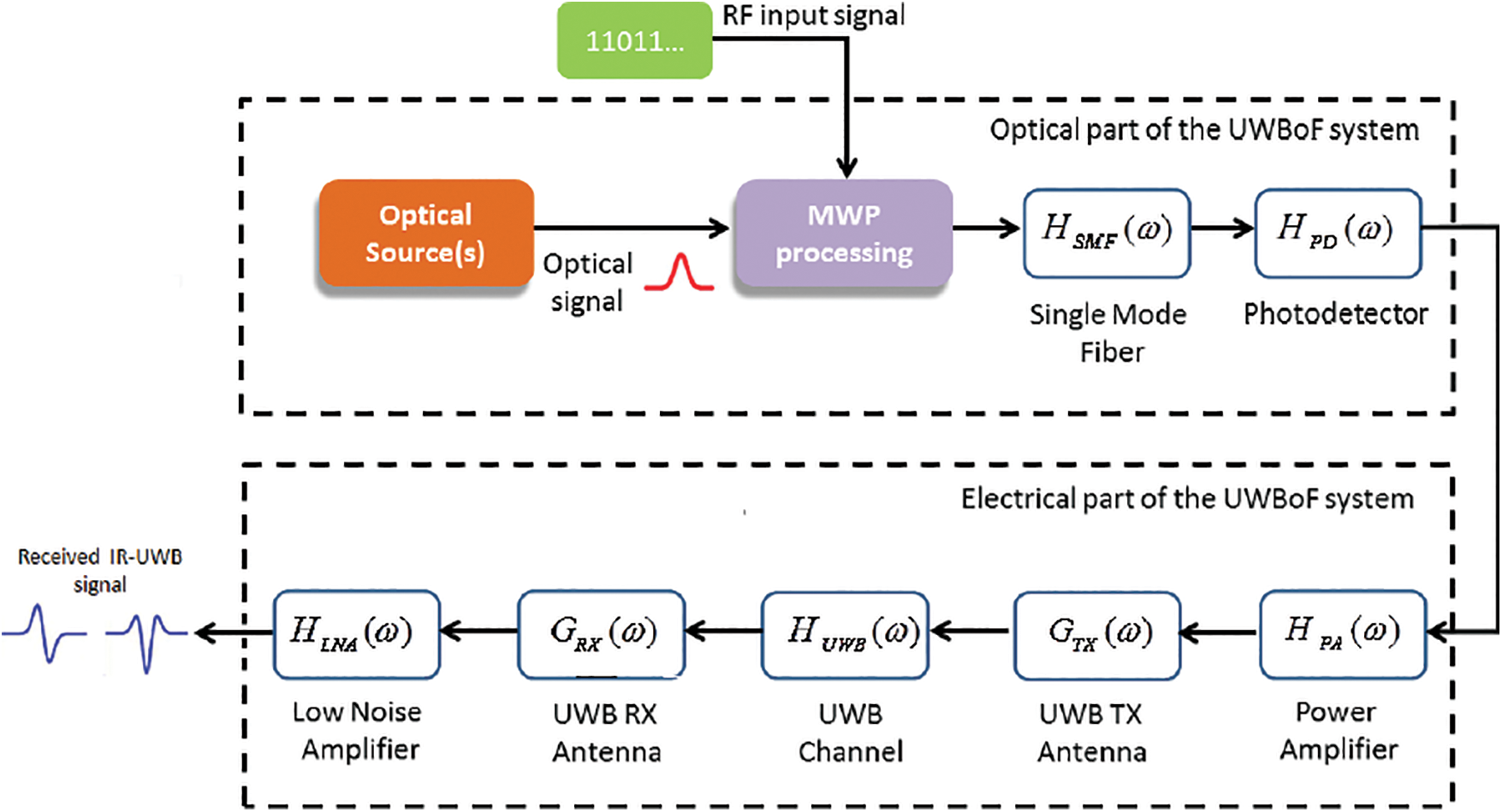
Radio optical network simulation tool (ronst)
This paper presents a radio optical network simulation tool (RONST) for modeling optical-wireless systems. For a typical optical and electrical chain environment, performance should be optimized concurrently before system implementation. As a result, simulating such systems turns out to be a multidisciplinary problem. The governing equations are incompatible with co-simulation in the traditional environments of existing software (SW) packages. The ultra-wideband (UWB) technology is an ideal candidate for providing high-speed short-range access for wireless services. The limited wireless reach
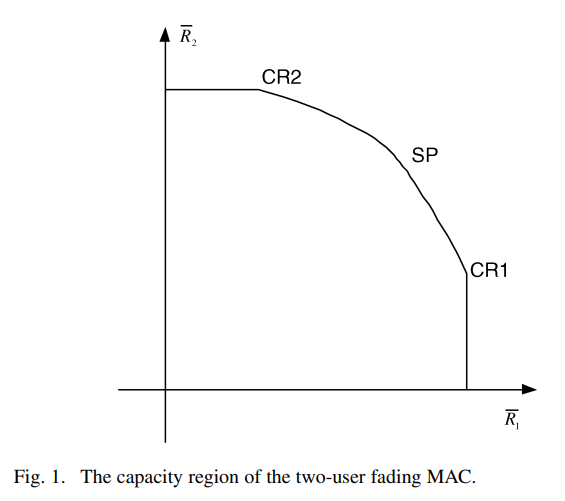
The water-filling game in fading multiple-access channels
A game-theoretic framework is developed to design and analyze the resource allocation algorithms in fading multiple-access channels (MACs), where the users are assumed to be selfish, rational, and limited by average power constraints. The maximum sum-rate point on the boundary of the MAC capacity region is shown to be the unique Nash equilibrium of the corresponding water-filling game. This result sheds a new light on the opportunistic communication principle. The base station is then introduced as a player interested in maximizing a weighted sum of the individual rates. A Stackelberg
Network-coded wireless powered cellular networks: Lifetime and throughput analysis
In this paper, we study a wireless powered cellular network (WPCN) supported with network coding capability. In particular, we consider a network consisting of k cellular users (CUs) served by a hybrid access point (HAP) that takes over energy transfer to the users on top of information transmission over both the uplink (UL) and downlink (DL). Each CU has k+1 states representing its communication behavior, and collectively are referred to as the user demand profile. Opportunistically, when the CUs have information to be exchanged through the HAP, it broadcasts this information in coded format
Reliability and Security Analysis of an Entanglement-Based QKD Protocol in a Dynamic Ground-to-UAV FSO Communications System
Quantum cryptography is a promising technology that achieves unconditional security, which is essential to a wide range of sensitive applications. In contrast to optical fiber, the free-space optical (FSO) link is efficiently used as a quantum channel without affecting the polarization of transmitted photons. However, the FSO link has several impairments, such as atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors, which affect the performance of the quantum channel. This paper proposes a quantum key distribution (QKD) scheme that uses a time-bin entanglement protocol over the FSO channel that suffers
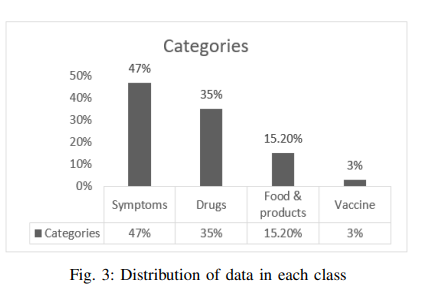
Intelligent Arabic-Based Healthcare Assistant
Text classification has been one of the most common natural language processing (NLP) objectives in recent years. Compared to other languages, this mission with Arabic is relatively restricted and in its early stages, and this combination in the medical application area is rare. This paper builds an Arabic health care assistant, specifically a pediatrician that supports Arabic dialects, especially Egyptian accents. The proposed application is a chatbot based on Artificial Intelligence (AI) models after experimenting with Two Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) models
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 14
- Next page ››
