Breadcrumb
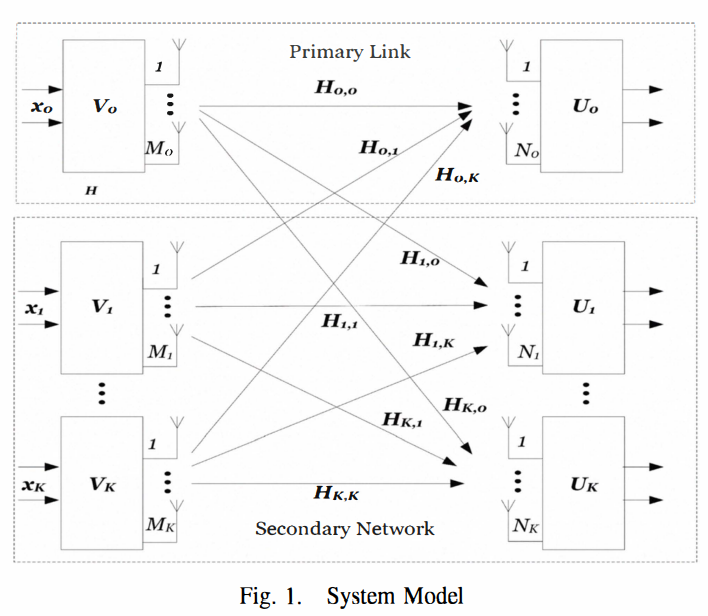
Opportunistic interference alignment for multiuser cognitive radio
We present an interference alignment (IA) technique that allows multiple opportunistic transmitters (secondary users) to use the same frequency band of a pre-existing primary link without generating any interference. The primary and secondary transmit-receive pairs are equipped with multiple antennas. We exploit the fact that under power constraints on the primary transmitter, the rate of the primary user is maximized by water-filling on the singular values of its channel matrix leaving some eigen modes unused. The secondary users can align their transmitted signals to produce a number of
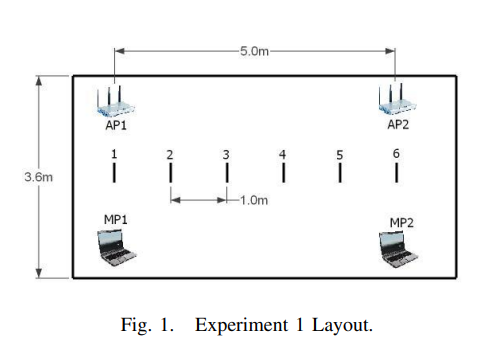
Analysis of a device-free passive tracking system in typical wireless environments
Device-free Passive (DfP) localization is a new concept in location determination where the tracked entity does not carry any device nor participate actively in the localization process. A DfP system operates by processing the received physical signal of a wireless transmitter at one or more monitoring points. The previously introduced DfP system was shown to enable the tracking of a single intruder with high accuracy in a highly controlled WLAN environment. In this paper, we propose and analyze different algorithms for DfP tracking in a typical indoor WLAN environment, rich in multipath. We
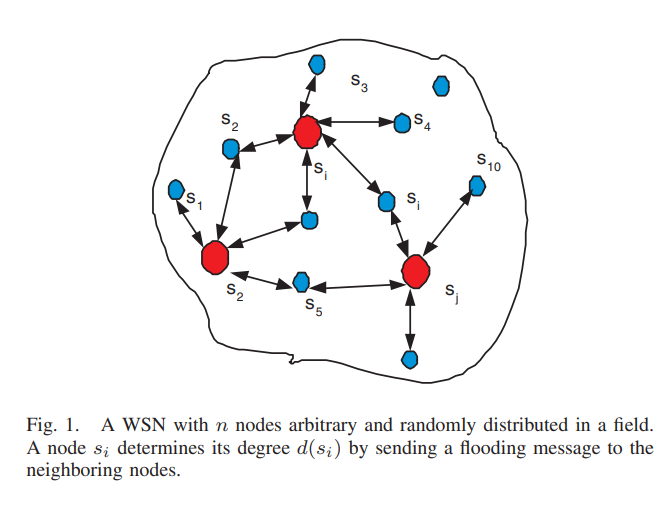
Distributed flooding-based storage algorithms for large-scale wireless sensor networks
In this paper we propose distributed storage algorithms for large-scale wireless sensor networks. Assume a wireless sensor network with n nodes that have limited power, memory, and bandwidth. Each node is capable of both sensing and storing data. Such sensor nodes might disappear from the network due to failures or battery depletion. Hence it is desired to design efficient schemes to collect data from these n nodes. We propose two distributed storage algorithms (DSA's) that utilize network flooding to solve this problem. In the first algorithm, DSA-I, we assume that the total number of sensors
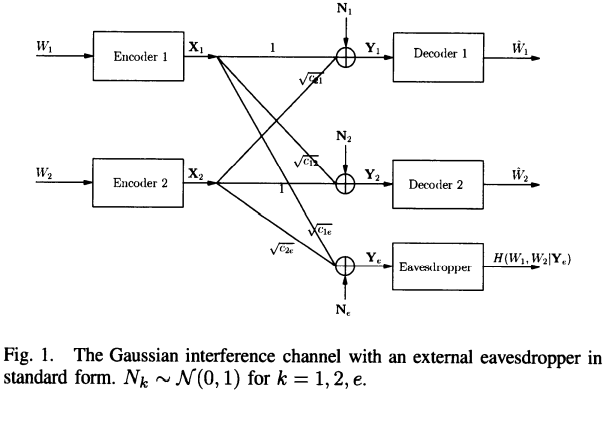
On the secrecy rate region for the interference channel
This paper studies interference channels with security constraints. The existence of an external eavesdropper in a two-user interference channel is assumed, where the network users would like to secure their messages from the external eavesdropper. The cooperative binning and channel prefixing scheme is proposed for this system model which allows users to cooperatively add randomness to the channel in order to degrade the observations of the external eavesdropper. This scheme allows users to add randomness to the channel in two ways: 1) Users cooperate in their design of the binning codebooks
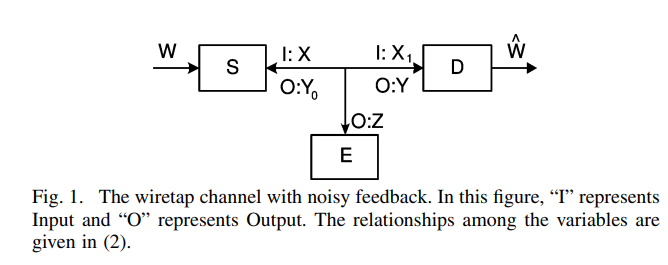
The wiretap channel with feedback: Encryption over the channel
In this work, the critical role of noisy feedback in enhancing the secrecy capacity of the wiretap channel is established. Unlike previous works, where a noiseless public discussion channel is used for feedback, the feed-forward and feedback signals share the same noisy channel in the present model. Quite interestingly, this noisy feedback model is shown to be more advantageous in the current setting. More specifically, the discrete memoryless modulo-additive channel with a full-duplex destination node is considered first, and it is shown that the judicious use of feedback increases the
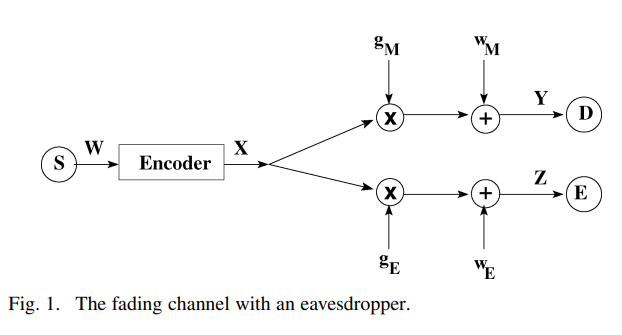
On the secrecy capacity of fading channels
We consider the secure transmission of information over an ergodic fading channel in the presence of an eavesdropper. Our eavesdropper can be viewed as the wireless counterpart of Wyner's wiretapper. The secrecy capacity of such a system is characterized under the assumption of asymptotically long coherence intervals. We first consider the full channel state information (CSI) case, where the transmitter has access to the channel gains of the legitimate receiver and the eavesdropper. The secrecy capacity under this full CSI assumption serves as an upper bound for the secrecy capacity when only
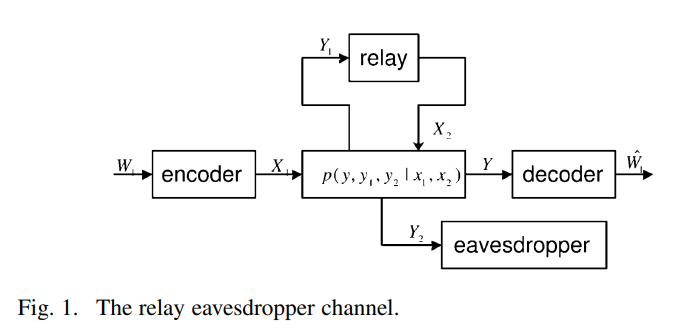
The relay-eavesdropper channel: Cooperation for secrecy
This paper establishes the utility of user cooperation in facilitating secure wireless communications. In particular, the four-terminal relay-eavesdropper channel is introduced and an outer-bound on the optimal rate-equivocation region is derived. Several cooperation strategies are then devised and the corresponding achievable rate-equivocation region are characterized. Of particular interest is the novel noise-forwarding (NF) strategy, where the relay node sends codewords independent of the source message to confuse the eavesdropper. This strategy is used to illustrate the deaf helper
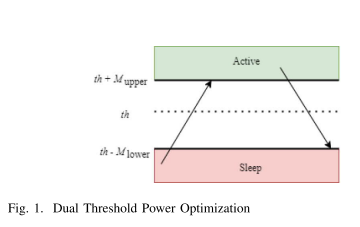
Optimal Power Consumption on Distributed Edge Services Under Non-Uniform Traffic with Dual Threshold Sleep/Active Control
Mobile edge computing (MEC) is a key enabling technology for supporting high-speed and low latency services in the fifth generation (5G) and beyond networks. MEC paradigm moves computational resources from centralized cloud servers towards the edge of the network, nearer to the users. However, edge computation resources increase the power consumption of the network. Moreover, the non-uniform traffic load on the edge servers causes resources to be underutilized and decrease the system's power efficiency. To achieve the green networking concept encouraged in 5G and beyond networks, unused MEC
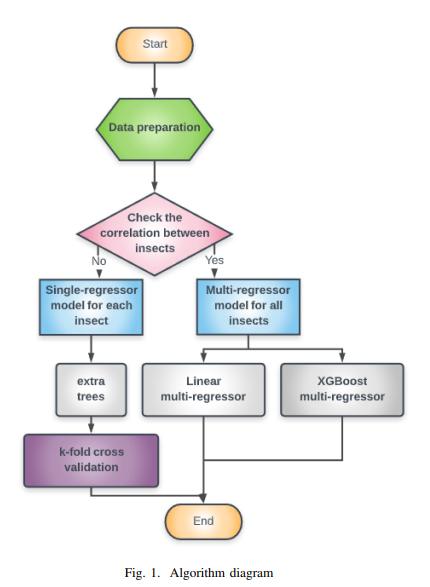
Guava Trees Disease Monitoring Using the Integration of Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics
The increase in population, food demand, and the pollution levels of the environment are considered major problems of this era. For these reasons, the traditional ways of farming are no longer suitable for early and accurate detection of biotic stress. Recently, precision agriculture has been extensively used as a potential solution for the aforementioned problems using high resolution optical sensors and data analysis methods that are able to cope with the resolution, size and complexity of the signals from these sensors. In this paper, several methods of machine learning have been utilized

Chaos-Based RNG using Semiconductor Lasers with Parameters Variation Tolerance
Random numbers play an essential role in guaranteeing secrecy in most cryptographic systems. A chaotic optical signal is exploited to achieve high-speed random numbers. It could be generated by using one or more semiconductor lasers with external optical feedback. However, this system faces two major issues, high peak to average power ratio (PAPR) and parameter variations. These issues highly affected the randomness of the generated bitstreams. In this paper, we use a non-linear compression technique to compand the generated signal before it is quantized to avoid the effects of the PAPR. Also
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 13
- Next page ››
