Breadcrumb
Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends
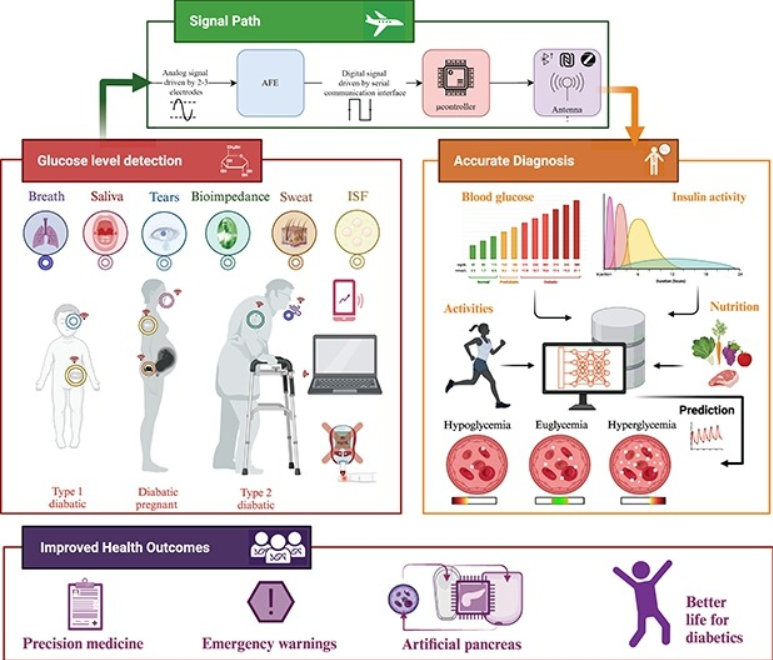
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood glucose levels and can cause damage to multiple organs over time. Continuous monitoring of glucose levels is essential for both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals. There have been major developments in glucose monitoring technology over the past decade, which have been driven by research and industry efforts. Despite these significant advancements, the area of glucose biosensors still faces significant challenges. This paper presents a comprehensive summary of the latest glucose monitoring technologies, including invasive
Liver Disease Diagnosis using Tree-Based Machine Learning Algorithms
Liver Disease (LD) is a lethal yet relatively common disorder that is impacting the lives of millions across the world, causing slow yet irreversible internal organ damage or total organ failure if left untreated. In this study, LD is determined as the damage a Liver sustained due to excessive drug or alcohol abuse and other causes which leave severe scarring on the Liver leading to permanent functionality loss or cancer. This study revolves around determining if a person suffers from the disease regardless of the stage of the disease. To detect and minimize the impact of LD, tree-based
Automatic Detection of Alzheimer Disease from 3D MRI Images using Deep CNNs
Alzheimer's disease (AD), also referred to simply as Alzheimer's, is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and worsens over time. It is the cause of 60% to 70% of cases of dementia. In 2015, there were approximately 29.8 million people worldwide with AD. It most often begins in people over 65 years of age as it affects about 6% of people 65 years and older, although 4% to 5% of cases are early-onset Alzheimer's which begin before this. In 2015, researchers have figured out that dementia resulted in about 1.9 million deaths. Continuous efforts are made to cure the

An Optimized Non-Invasive Blood Glucose and Temperature Body Measurement System
Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not adequately process food for energy production. Most of the food we consume is converted into glucose, or sugar, which our bodies use for energy. Moreover, the pancreas, which is an organ located near the stomach, produces insulin, a hormone that aids in the transport of glucose into our bodies' cells. Diabetes occurs when your body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use its own insulin the way it is supposed to. Sugars accumulate in your blood as a result of this. This is why diabetes is often referred to as "sugar". People with
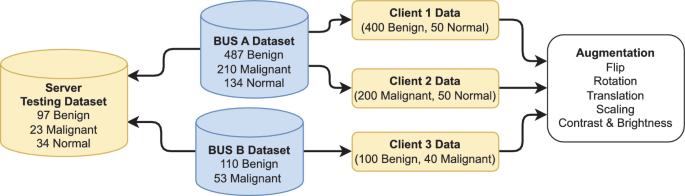
A Novel Approach to Breast Cancer Segmentation Using U-Net Model with Attention Mechanisms and FedProx
Breast cancer is a leading cause of death among women worldwide, emphasizing the need for early detection and accurate diagnosis. As such Ultrasound Imaging, a reliable and cost-effective tool, is used for this purpose, however the sensitive nature of medical data makes it challenging to develop accurate and private artificial intelligence models. A solution is Federated Learning as it is a promising technique for distributed machine learning on sensitive medical data while preserving patient privacy. However, training on non-Independent and non-Identically Distributed (non-IID) local datasets

Energy Aware Tikhonov-Regularized FPA Technique for Task Scheduling in Wearable Biomedical Devices
Harvesting the energy from environmental sources is a promising solution for perpetual and continuous operation of biomedical wearable devices. Although the energy harvesting technology ensures the availability of energy source, yet power management is crucial to ensure prolonged and stable operation under a stringent power budget. Thus, power-aware task scheduling can play a key role in minimizing energy consumption to improve system durability while maintaining device functionality. This chapter proposes a novel biosensor task scheduling of energy harvesting-based biomedical wearable devices
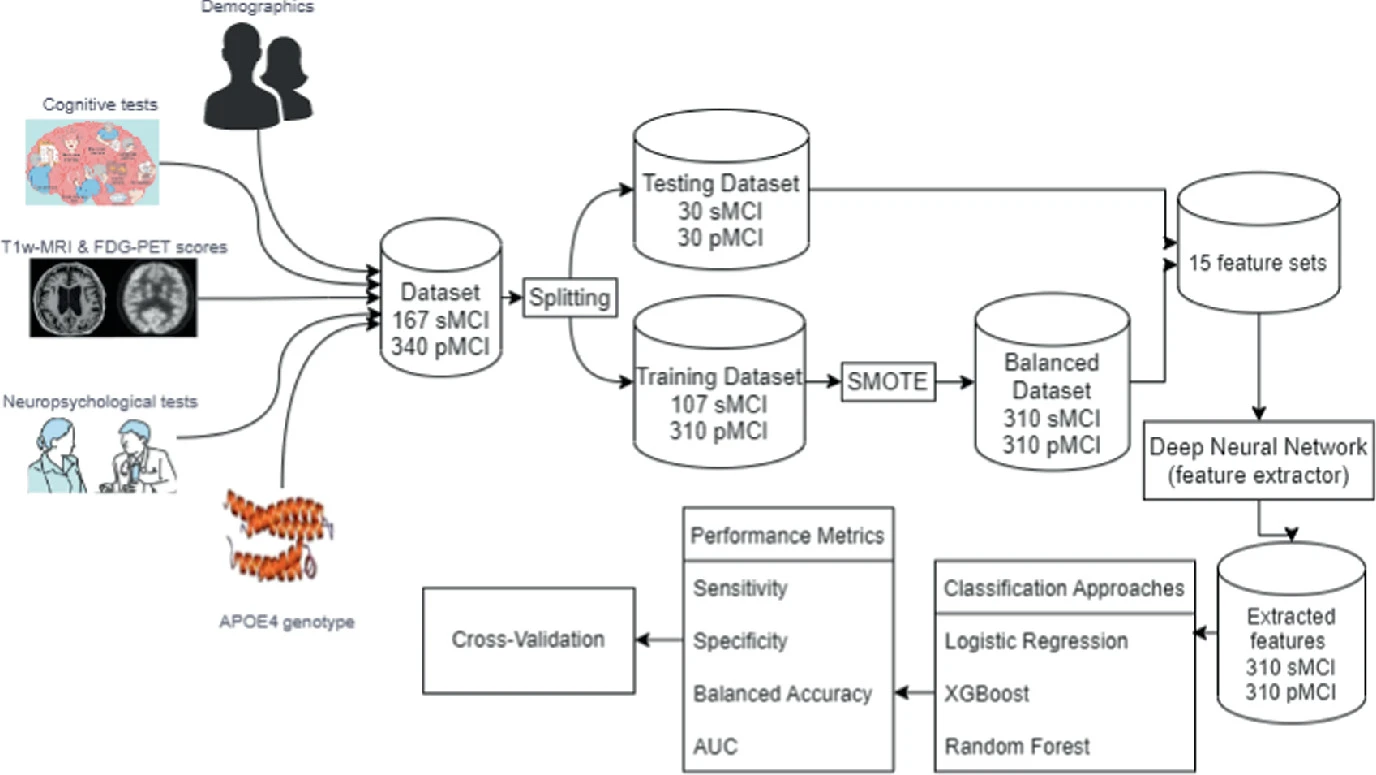
A Novel Diagnostic Model for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Clinical and Neuroimaging Features
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a dangerous disease that is known for its characteristics of eroding memory and destroying the brain. The classification of Alzheimer's disease is an important topic that has recently been addressed by many studies using Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) methods. Most research papers tackling early diagnosis of AD use these methods as a feature extractor for neuroimaging data. In our research paper, the proposed algorithm is to optimize the performance of the prediction of early diagnosis from the multimodal dataset by a multi-step framework that uses a

Sustainable Energy-Aware Task Scheduling for Wearable Medical Device Using Flower Pollination Algorithm
Power management and energy conservation are crucial for medical wearable devices that rely on energy harvesting. These devices operate under strict power budgets and require prolonged and stable operation. To achieve this, Energy-aware task scheduling is proposed as a solution to minimize energy consumption while ensuring the continued operational capabilities of the device. our paper presents a task scheduling method using the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA). The proposed task scheduling focuses on managing the activity of key components such as the heart rate sensor, temperature sensor

Improvement of piezoresistive pressure sensor using zig-zag shaped and PVDF material
Due to a wide range of applications in the biomedical industry, the need for flexible and wearable sensors is growing every day. A pressure sensor generates a signal based on the applied pressure. Sensors have become an integral component of our daily lives, from personal gadgets to industrial machinery. The identification of the low signal from the body necessitates the use of particularly sensitive sensors. The development of a pressure sensor that can transform the maximum input signal into an electrical output is critical. In this paper, zig-zag piezoresistors on a square diaphragm were
An Efficient DMO Task Scheduling Technique for Wearable Biomedical Devices
The popularity of wearable devices has grown as they improve the quality of life in many applications. In particular, for medical devices, energy harvesters are the dominating source of energy for wearable devices. However, their power budget is limited. Thus, power-saving techniques are essential components in the whole technology stack of those devices. That is, choosing the optimal schedule for different tasks running on the wearable device can help to reduce energy consumption. This paper presents a sensor task scheduling technique for optimizing energy consumption for energy harvesting
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››
