Breadcrumb
On orthogonal band allocation for multiuser multiband cognitive radio networks: Stability analysis
In this work, we study the problem of band allocation of Mi buffered (i.e., with data queues capable of storing incoming traffic packets) secondary users (SUs) to Mp primary frequency bands licensed to (owned by) Mp buffered primary users. The bands are assigned to SUs in an orthogonal (one-to-one) fashion, such that neither band sharing nor multiband allocations are permitted. In order to study the stability region of the secondary network, the optimization problem used to obtain the stability region's envelope (closure) is established and is shown to be a linear program, which can be solved

Achievable secrecy rate regions for the two-way wiretap channel
The two-way wiretap channel is considered in this paper. Two legitimate users, Alice and Bob, wish to exchange messages securely in the presence of a passive eavesdropper Eve. In the full-duplex scenario, where each node can transmit and receive simultaneously, new achievable secrecy rate regions are obtained based on the idea of allowing the two users to jointly optimize their channel prefixing distributions and binning codebooks in addition to key sharing. The new regions are shown to be strictly larger than the known ones for a wide class of discrete memoryless and Gaussian channels. In the
On the coexistence of a primary user with an energy harvesting secondary user: A case of cognitive cooperation
In this paper, we consider a cognitive scenario where an energy harvesting secondary user shares the spectrum with a primary user. The secondary source helps the primary source in delivering its undelivered packets during periods of silence of the primary source. The primary source has a queue for storing its data packets, whereas the secondary source has two data queues: a queue for storing its own packets and the other for storing the fraction of the undelivered primary packets accepted for relaying. The secondary source is assumed to be a battery-based node, which harvests energy packets
A proper throughput-leakage balance for downlink cellular networks
A novel transmission scheme is developed for the downlink frame of cellular networks. Each base station (BS) aims at iteratively balancing the throughput at the mobile stations (MSs) of its cell with the interference it causes at the MSs of the neighboring cells, requiring negligible coordination between the BSs. A simplified version of the scheme that neither requires iterations nor cooperation is also proposed. Simulation results show that the proposed schemes achieve substantial gains over well-known schemes in the literature. © 2014 IEEE.
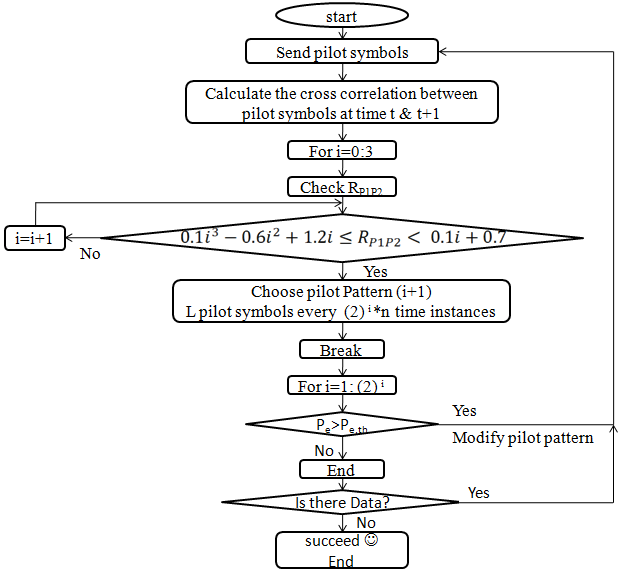
A new adaptive channel estimation for frequency selective time varying fading OFDM channels
In this paper a new algorithm for adaptive dynamic channel estimation for frequency selective time varying fading OFDM channels is proposed. The new algorithm adopts a new strategy that successfully increases OFDM symbol rate. Instead of using a fixed training pilot sequence, the proposed algorithm uses a logic controller to choose among several available training patterns. The controller choice is based on the cross-correlation between pilot symbols over two consecutive time instants (which is considered to be a suitable measure of channel stationarity) as well as the deviation from the
Soft-sensing CQI feedback-based access scheme in cognitive radio networks
In this paper, an access scheme for cognitive radio networks is proposed in which secondary users (SUs) make use of the primary user(s) (PUs) channel quality feedback information. SUs decide their transmission strategy based on the PUs' channel quality indicator (CQI) feedback available in the PU network and the SUs' sensing of PUs' activity. We consider two energy sensing approaches, namely, hard-sensing, and soft-sensing. An SU accesses the primary channel with access probabilities which are selected to maximize the SU service rate while ensuring PUs' quality of service requirements defined
A novel binary gaining–sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm for feature selection
To obtain the optimal set of features in feature selection problems is the most challenging and prominent problem in machine learning. Very few human-related metaheuristic algorithms were developed and solved this type of problem. It motivated us to check the performance of recently developed gaining–sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm (GSK), which is based on the concept of gaining and sharing knowledge of humans throughout their lifespan. It depends on two stages: beginners–intermediate gaining and sharing stage and intermediate–experts gaining and sharing stage. In this study
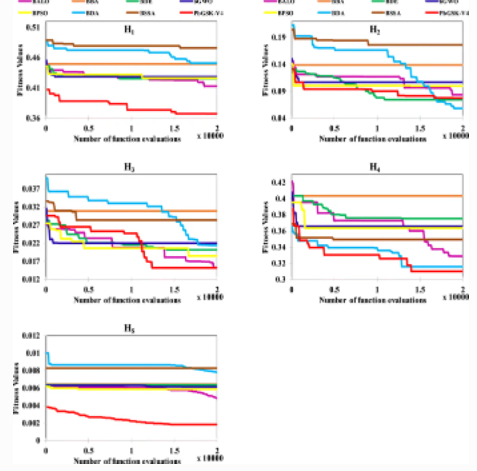
S-shaped and V-shaped gaining-sharing knowledge-based algorithm for feature selection
In machine learning, searching for the optimal feature subset from the original datasets is a very challenging and prominent task. The metaheuristic algorithms are used in finding out the relevant, important features, that enhance the classification accuracy and save the resource time. Most of the algorithms have shown excellent performance in solving feature selection problems. A recently developed metaheuristic algorithm, gaining-sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm (GSK), is considered for finding out the optimal feature subset. GSK algorithm was proposed over continuous search
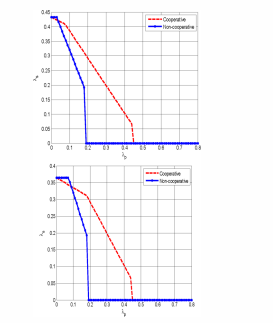
Stability analysis for multi-user cooperative cognitive radio network with energy harvesting
This paper deals with stability analysis for cognitive cooperative system composed of one primary user and many secondary users with energy harvesting imposed at both primary and secondary users. Secondary users are grouped in a cluster with a cluster supervision block (CSB) controller which controls and synchronizes all the activities of the SU cluster. The secondary user cluster is equipped with a common relay queue for collaboration with the PU. Multiple SUs cooperate with one PU for its data transmission, getting mutual benefits for both users, such that, the PU exploits SUs' power and
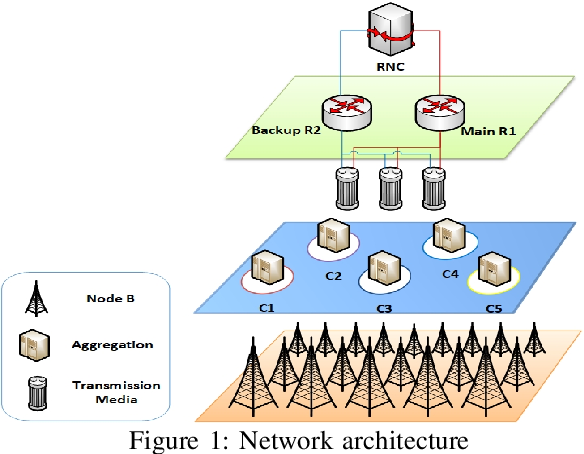
Learning of mobile-traffic patterns for resource management and dynamic power controlling
Recently, the topology control solutions that use static transmission power, transmission range, and link quality, might not be useful. The objective of this paper adapts the transmission power to be adjusted with external changes by applying a machine learning algorithms. We develop a traffic signature algorithm based on traffic clusters of the network sites that have the same behavior then we predict their upcoming changes and correspondingly. The contribution of this work is using this model to create an optimal power distribution function based on traffic load. Furthermore, we propose a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 20
- Next page ››

