Breadcrumb
Dynamic Traffic Model with Optimal Gateways Placement in IP Cloud Heterogeneous CRAN
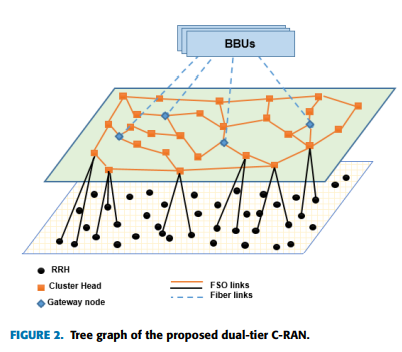
In this paper, topology design, optimal routing, and gateways placement selection algorithms are proposed in Heterogeneous Cloud Radio Access Network (C-RAN) with exploiting Free Space Optical (FSO) communication. The proposed network consists of two tiers; the lower tier concerns with clustering Remote Radio Heads (RRHs) based on traffic demands. The upper tier consists of transceivers along with the Cluster Heads (CHs) and gateways. Algorithms are proposed to achieve the lowest number of edges and the highest possible throughput based on the presented optimization problem. Moreover, route
Demonstration of Forward Collision Warning System Based on Real-Time Computer Vision
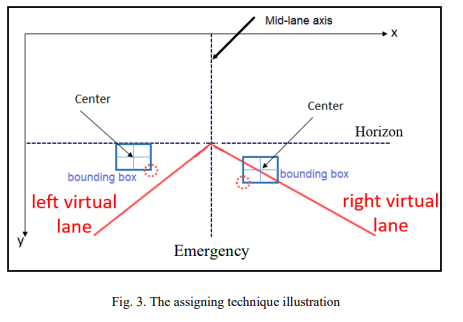
This paper demonstrates the software and hardware of a forward-collision warning system using techniques of realtime computer vision which helps self-driving cars and autonomous vehicles systems to merge with the road environment safely and ensure the reliability of these systems. The software approach of the paper consists of five parts: car detection, depth estimation, lane assignation, the relative speed of other cars and their corresponding speed limit and finally ultrasonic sensors which completes the front of the vehicle as the camera can't cover it alone. Besides these five objectives
6G: A comprehensive survey on technologies, applications, challenges, and research problems
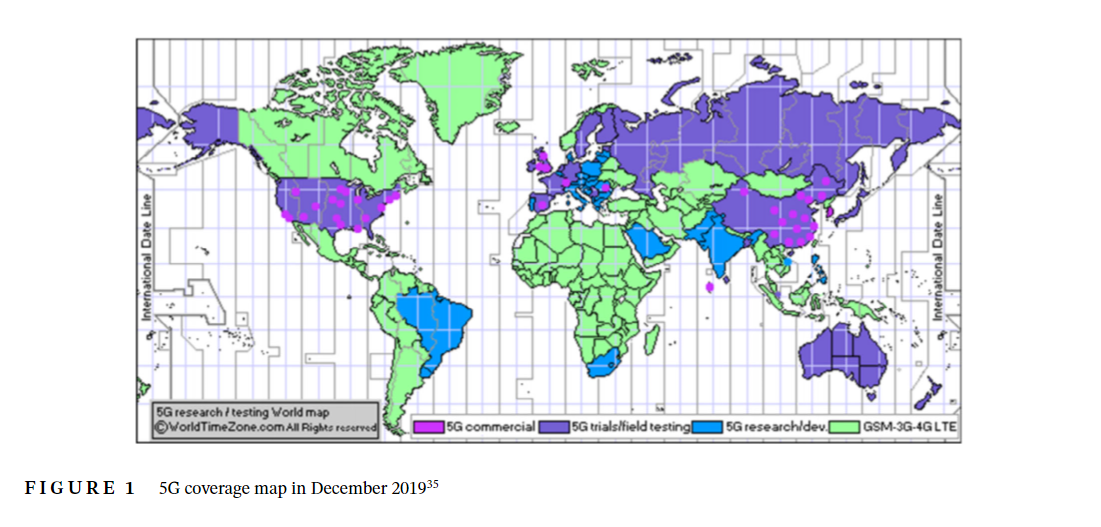
The inherent limitations of the network keep on going to be revealed with the continuous deployment of cellular networks. The next generation 6G is motivated by these drawbacks to properly integrate important rate-hungry applications such as extended reality, wireless brain-computer interactions, autonomous vehicles, and so on. Also, to support significant applications, 6G will handle large amounts of data transmission in smart cities with much lower latency. It combines many state-of-the-art trends and technology to provide higher data rates for ultra-reliable and low latency communications
Generic evaluation of FSO system over Málaga turbulence channel with MPPM and non-zero-boresight pointing errors
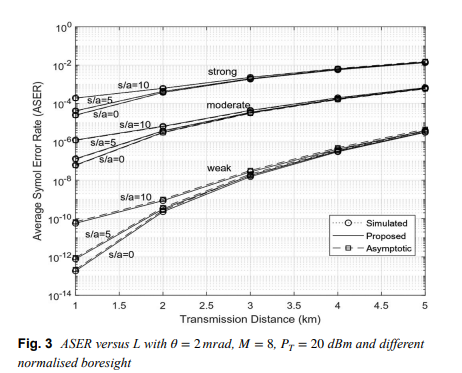
Free space optical (FSO) communication channels are affected by fluctuations in irradiance due to atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors. Recently, a generalized statistical model knows as Málaga (M) was developed to describe irradiance fluctuations of the beam propagating through a turbulent medium. In this paper, an approximate finite-series probability density function (PDF) for composite M turbulence with pointing errors is verified. Considering multiple pulseposition- modulation (MPPM) with intensity modulation and direct detection, specific closed-form expressions for average symbol
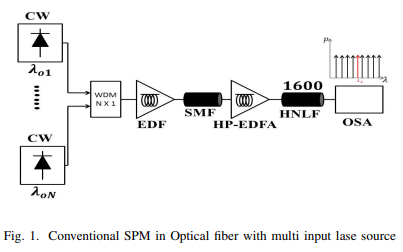
Generation of OFC by Self-Phase Modulation and Multiple Laser Sources in HNLF
Self-Phase Modulation (SPM) is a non-linear phenomenon relating to the self-induced phase shift encountered by the optical field during its transmission into the optical fiber. It is the most popular technique for generating an optical frequency comb (OFC) with different frequency spacing values. The SPM is regulated by many parameters such as fiber length, input optical power, and the non-linearity of the optical fiber. The OFC distinguishes between a high spectral flatness level, a high optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) and a wide range of wavelengths. In this paper, The SPM uses to
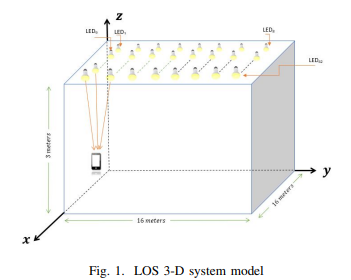
Visible Light Communications Localization Error Enhancement using Parameter Relaxation
In this paper, we propose applying a parameter relaxation technique to the location estimation algorithm that is based on the Received Signal Strength (RSS) of Visible Light Communications (VLC). A hybrid system of localization balancing is introduced, where the localization algorithm is developed with and without this efficient parameter relaxation. The results show that applying the parameter relaxation reduces the localization Root Mean Square (RMS) error by 43% of that without relaxation; and the processing time is reduced by 18% of that without relaxation. Moreover, the parameter
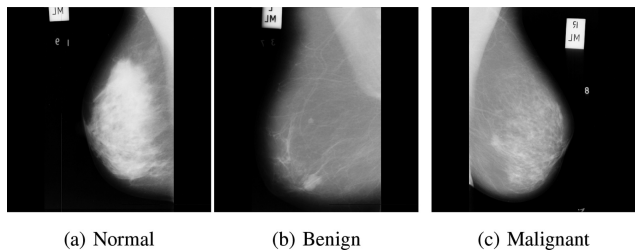
Early breast cancer diagnostics based on hierarchical machine learning classification for mammography images
Breast cancer constitutes a significant threat to women’s health and is considered the second leading cause of their death. Breast cancer is a result of abnormal behavior in the functionality of the normal breast cells. Therefore, breast cells tend to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor that can be felt like a breast lump. Early diagnosis of breast cancer is proved to reduce the risks of death by providing a better chance of identifying a suitable treatment. Machine learning and artificial intelligence play a key role in healthcare systems by assisting physicians in diagnosing early, better
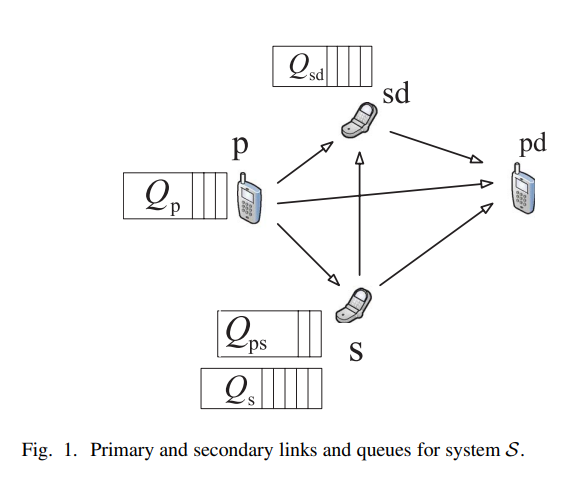
Maximum Secondary Stable Throughput of a Cooperative Secondary Transmitter-Receiver Pair: Protocol Design and Stability Analysis
In this paper, we investigate the impact of cooperation between a secondary transmitter-receiver pair and a primary transmitter on the maximum stable throughput of the primary-secondary network. Each transmitter, either primary or secondary, has a buffer for storing its own traffic. In addition to its own buffer, the secondary transmitter has a buffer for storing a fraction of the undelivered primary packets due to channel impairments. Moreover, the secondary destination has a relaying queue (buffer) for storing a fraction of the undelivered primary packets. In our proposed cooperative system
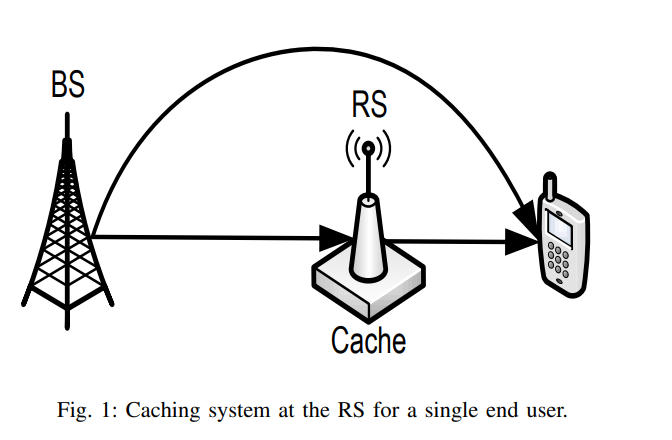
On Optimal Dynamic Caching in Relay Networks
We investigate dynamic content caching in relay networks where an intermediate relay station (RS) can adaptively cache data content based on their varying popularity. With the objective of minimizing the time average cost of content delivery, we formulate and study the problem of optimal RS cache allocation when the popularities of data content are unknown apriori to the network. While optimal dynamic cache control suffers the curse of dimensionality, we develop a fundamental lower bound on the achievable cost by any caching policy. Inspired by the structure of such lower bound, we develop a
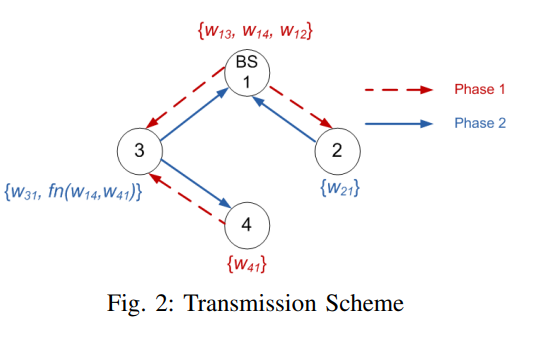
Degrees of freedom region of device-relaying cellular network
In this paper, we characterize the degrees of freedom (DoF) region of a MIMO device-relaying cellular network (DRCN) with three users and one base station (BS), where each user exchanges unicast messages with the BS. We assume that one of the users has no direct link to the BS, and hence, device-relaying is utilized to exchange data between this user and the BS, i.e., data is relayed via another user which has a direct link to the BS and a device to device (D2D) link to this user. We assume that each node operates in perfect full-duplex mode. Cut-set and genie-aided bounds are utilized to
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››

