Breadcrumb
Optimum Selection of Communication Tower Structures Based on Wind Loads & lifecycle cost analysis
Communication towers are vital assets in our daily lives as they transfer signals between cell phones facilitating communication and commerce among people and businesses all around the world. Wind loads are crucial in the communication towers design since they are tall and slender. With climate change bringing more storms and higher wind speeds, it is more crucial to research the finest tower structure that withstands such conditions with the least life cycle cost. Therefore, in this paper, a comparative case study is performed between 45 m height lattice tower and monopole tower in Egypt. Two

Apache Spark Powered: Enhancing Network Intrusion Detection System Using Random Forest
The increasing sophistication of cyber attacks necessitates effective intrusion detection systems. We propose a novel intrusion detection method integrating deep learning with big data management using Apache Spark. Leveraging the comprehensive CSE-CIC-IDS2018 dataset, we apply extensive data preprocessing, including handling missing and unreliable values, duplicates, and redundant columns. In addition, implementation of a Random Forest based feature importance approach is derived to prioritize the most impactful Features. Furthermore, stratified k-fold cross-validation is used for a model
Comparative Analysis of Wind-loaded Telecom Tower Structures with Recommendations
Telecommunication towers are essential infrastructure in today's fast-paced world. Lattice self-supporting towers, monopole towers, and guyed towers are the three types of structures that can be used for telecommunications towers. When analyzing telecom tower loads, wind loads are the most important ones to address. As a result, it is necessary to choose an appropriate structure that can withstand the wind and the surrounding environment. The main aim of this paper is to propose a guideline for selecting the optimum tower structure based on the surrounding environment. In order to create this

Relay Selection in NOMA-Based Cooperative Wireless Backhaul Networks
The joint application of wireless backhaul networks and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) hold the potential to fulfill the increasing demands of fifth-generation (5G) communication networks and beyond. It is usual in wireless backhaul networks to take assistance from small cell base stations acting as intermediate relays to reach the remote destination. This cooperative communication is an acknowledged technique to combat multi-path fading, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the reliability and capacity of wireless networks. This article studies the application of relay selection (RS)
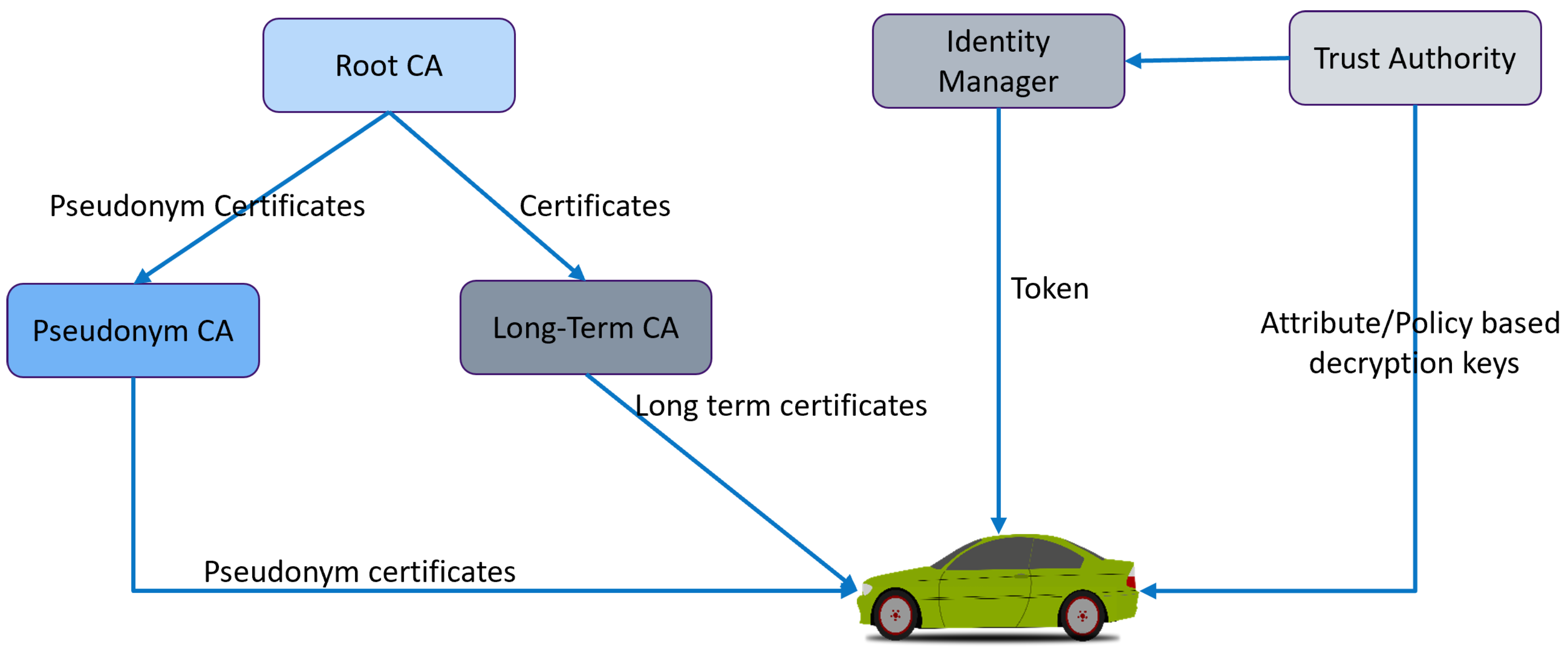
Developing Smart Control Platoon Algorithm for Secure VANET Environment
A vehicular ad hoc network (VANET) is a part of smart transportation. As a result of the vehicles being able to communicate with one another and share sensitive information, it is necessary to have an environment that can be trusted. Vehicles are clustered into platoons to ensure the secure transfer of information between them and select the platoon head of each platoon to control the vehicles. This paper proposes a smart control platoon system employing local and global trust schemes among vehicles in order to establish a secure environment. The platoon head calculates the local trust in each

Stability Analysis and Fault Detection of Telecommunication Towers Using Decision Tree Algorithm under Wind Speed Condition
This paper presents a decision tree (DT) modeling technique to estimate any increase in the load on telecommunication towers. A structural analysis was done for the lattice and mono-pole towers using TNX Tower software to determine the basic features of the towers, such as tilt angle, deflection, twist, and acceleration. The structure analysis generated a data set based on wind speeds. This data set was then used to train a machine-learning algorithm to estimate the loads on the structure. Any change in the applied loads greater than the loads considered in the design might be identified using

In the Identification of Arabic Dialects: A Loss Function Ensemble Learning Based-Approach
The automation of a system to accurately identify Arabic dialects many natural language processing tasks, including sentiment analysis, medical chatbots, Arabic speech recognition, machine translation, etc., will greatly benefit because it’s useful to understand the text’s dialect before performing different tasks to it. Different Arabic-speaking nations have adopted various dialects and writing systems. Most of the Arab countries understand modern standard Arabic (MSA), which is the native language of all other Arabic dialects. In this paper we propose a method for identifying Arabic dialects

Secure Data Aggregation in Cultural Heritage Monitoring: NMEC Case Study
Intelligent management plays a vital role in the preservation and success of cultural heritage, particularly in the context of museums. To ensure the long-term safeguarding of valuable and significant artifacts housed in museums, regular inspections are necessary. In this specific research study, the National Museum of Egyptian Civilization (NMEC) serves as a case study. To effectively monitor the museum's environment and protect its cultural assets, a wireless sensor network (WSN) is proposed. This network comprises various sensors that monitor crucial environmental factors such as
Light-Weight Face Mask Detector
People's lives have been severely disrupted recently due to the COVID-19 outbreak's fast worldwide proliferation and transmission. An option for controlling the epidemic is to make individuals wear face masks in public. For such regulation, automatic and effective face detection systems are required. A facial mask recognition model for real-time video-recorded streaming is provided in this research, which categorizes the pictures as (with mask) or (without mask). A dataset from Kaggle was used to develop and assess the model. The suggested system is computationally more precise, efficient and
Enhancing Spectral Efficiency of Ground-to-HAP FSO System with Adaptive MASK in Presence of Beam-wander and AoA Fluctuation
High Altitude Platform Station or HAP is an indispensable component for the upcoming wireless communication technologies. This paper presents an evaluation of the performance of a Ground-to-HAP communication system using free-space optical (FSO) technology. The performance of the system is determined by three factors: channel state, pointing error, and angle-of-arrival (AoA) fluctuation. Accordingly, the modulated-Gamma distribution is used as a channel modeling of the Ground-to-HAP uplink communication to analyze the effect of turbulence and beam wandering on the channel state. In this paper
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
