Breadcrumb
Alternate versus simultaneous relaying in MIMO cellular relay networks: A degrees of freedom study
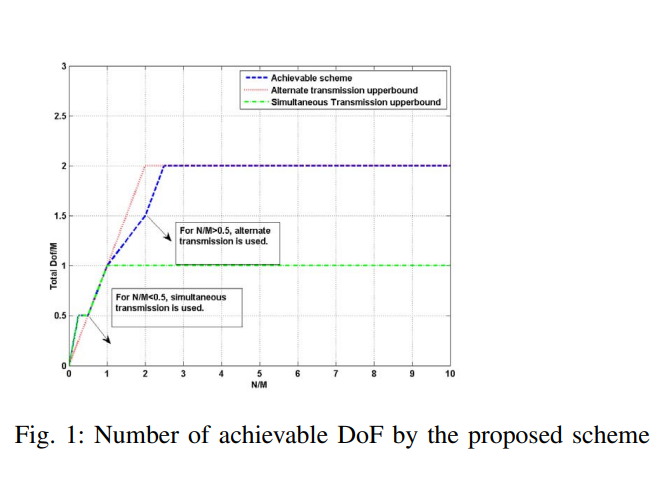
In this paper, a two-hop cellular relay network consisting of two source-destination pairs equipped with M antennas is considered where each source is assisted by two decode-and-forward relays operating in half-duplex mode and the relays are equipped with N antennas. The DoF of the system is investigated for both simultaneous and alternate relaying configurations. For each relay configuration, an outer bound on the degrees of freedom (DoF) is developed. A new achievable scheme is proposed that meets the upper bound on the maximum DoF for all values of M andN except for M
A degrees of freedom-optimal scheme for SISO X channel with synergistic alternating CSIT
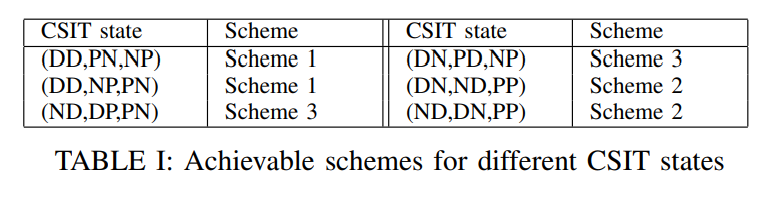
In this paper, the degrees of freedom (DoF) of the two-user single input single output (SISO) X channel are investigated. Three cases are considered for the availability of channel state information at the transmitters (CSIT); perfect, delayed, and no-CSIT. A new achievable scheme is proposed to elucidate the potency of interference creation-resurrection (IRC) when the available CSIT alternates between these three cases. For some patterns of alternating CSIT, the proposed scheme achieves 4/3 DoF, and hence, coincides with the information theoretic upper bound on the DoF of the X channel with
Distributed admission and power control for cognitive radios in spectrum underlay networks
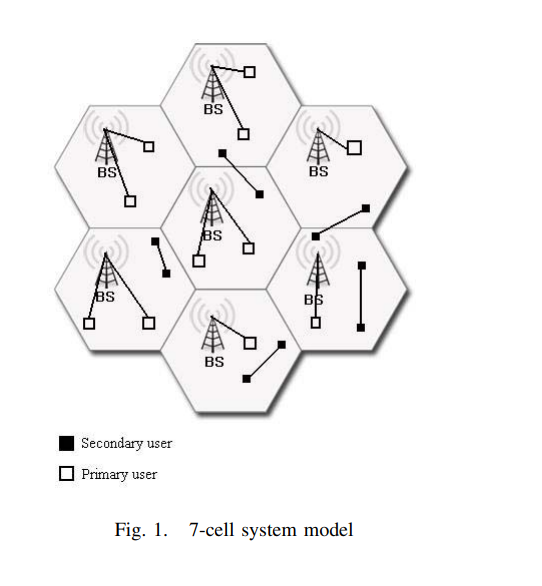
In this paper we investigate admission control and power allocation for cognitive radios in an underlay network. We consider the problem of maximizing the number of supported secondary links under their minimum QoS requirements without violating the maximum tolerable interference on primary receivers in a cellular network. An optimal solution to our problem is shown in previous works to be NP-hard. We propose an efficient distributed algorithm with reasonable complexity that provides results close to the optimum solution without requiring neither a large amount of signaling nor a wide range of
Towards energy efficient relay placement and load balancing in future wireless networks
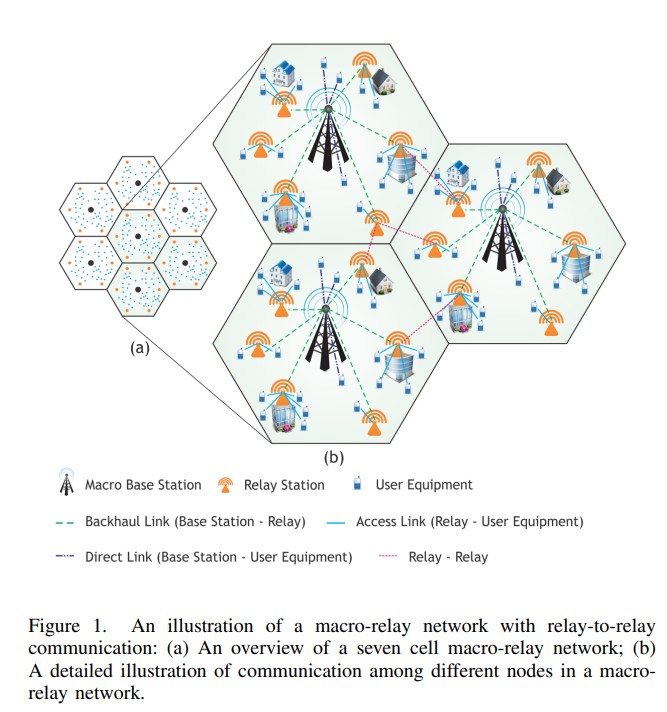
This paper presents an energy efficient relay deployment algorithm that determines the optimal location and number of relays for future wireless networks, including Long Term Evolution (LTE)-Advanced heterogeneous networks. We formulate an energy minimization problem for macro-relay heterogeneous networks as a Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) problem. The proposed algorithm not only optimally connects users to either relays or eNodeBs (eNBs), but also allows eNBs to switch into inactive mode. This is possible by enabling relay-to-relay communication which forms the basis for relays to
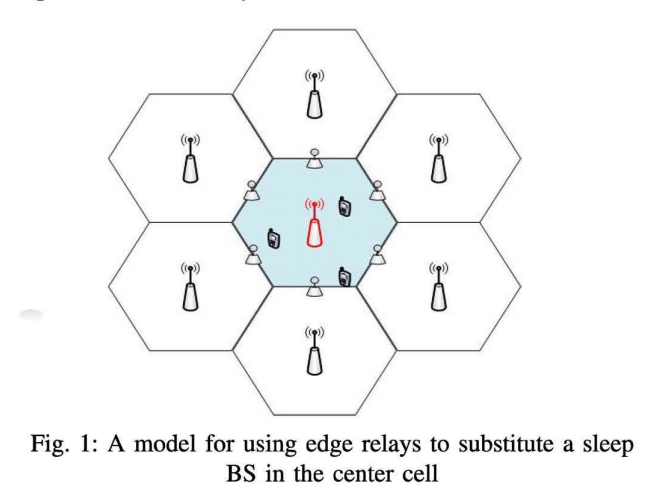
Joint relay assignment and adaptive modulation for energy-efficient cellular networks
Energy efficient operation of cellular systems becomes a core design goal for economic and environment-friendly network operation. Several studies have shown that the energy consumed in base stations represents 60-80% of the energy consumption in cellular networks. In this paper, we develop an optimization framework that exploits several energy efficient techniques including switching power modes of base stations, Adaptive Modulation (AM), and the use of relays. Our main objective is to reduce both, transmitted and circuit power, subject to satisfying the quality of service constraints. To
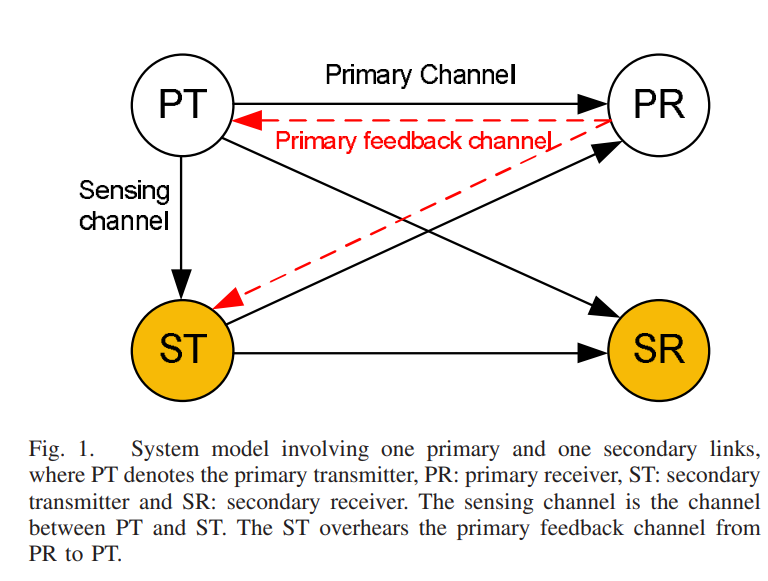
Leveraging primary feedback and spectrum sensing for cognitive access
We consider a time-slotted primary system where both the primary channel and primary activity are modeled as two independent two-state Markov chains. The primary transmitter can be idle or busy, whereas the channel can be in erasure or not. Moreover, the sensing channel between the primary transmitter and secondary transmitter is modeled as a two-state Markov chain to represent two levels of sensing reliability. At the beginning of each time slot, the secondary transmitter may remain idle, transmit directly, or probe the channel and access the channel only if it is sensed to be free. At the
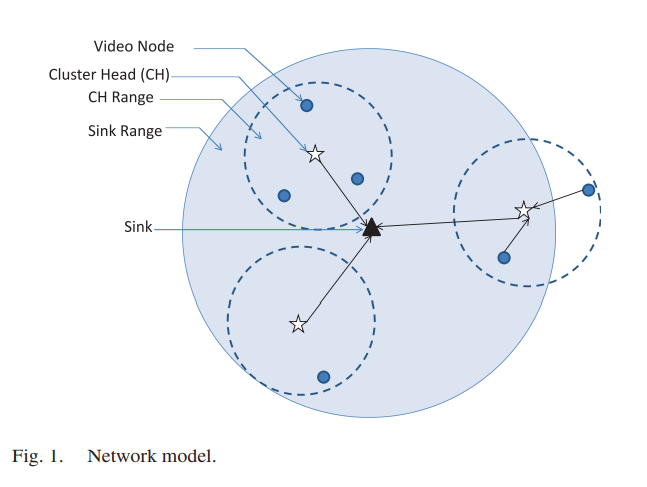
Optimal resource allocation for green and clustered video sensor networks
Wireless video sensor networks (WVSNs) are opening the door for many applications, such as industrial surveillance, environmental tracking, border security, and infrastructure health monitoring. In WVSN, energy conservation is very essential because: 1) sensors are usually battery-operated and 2) each sensor node needs to compress the video prior to transmission, which consumes more power than conventional wireless sensor networks. In this paper, we study the problem of minimizing the total power consumption in a cluster-based WVSN, leveraging cross-layer design to optimize the encoding power
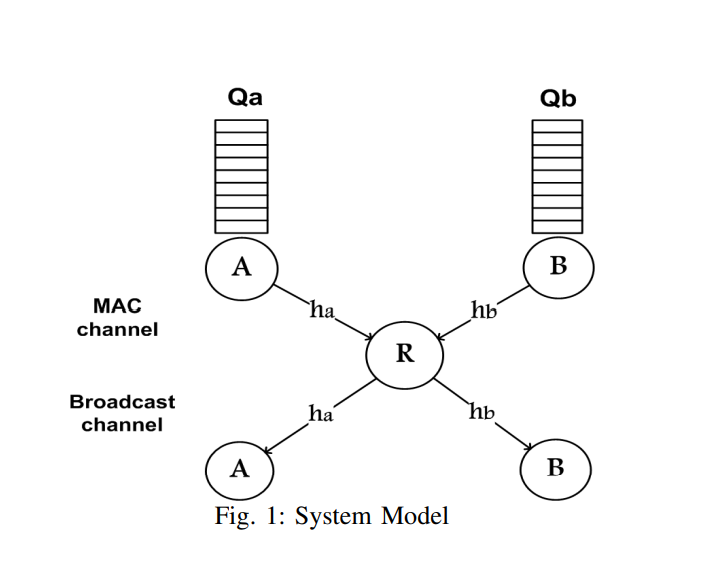
Maximum throughput opportunistic network coding in Two-Way Relay networks
In this paper, we study Two-Way Relaying (TWR) networks well-known for its throughput merits. In particular, we study the fundamental throughput delay trade-off in TWR networks using opportunistic network coding (ONC). We characterize the optimal ONC policy that maximizes the aggregate network throughput subject to an average packet delay constraint. Towards this objective, first, we consider a pair of nodes communicating through a common relay and develop a two dimensional Markov chain model capturing the buffers' length states at the two nodes. Second, we formulate an optimization problem
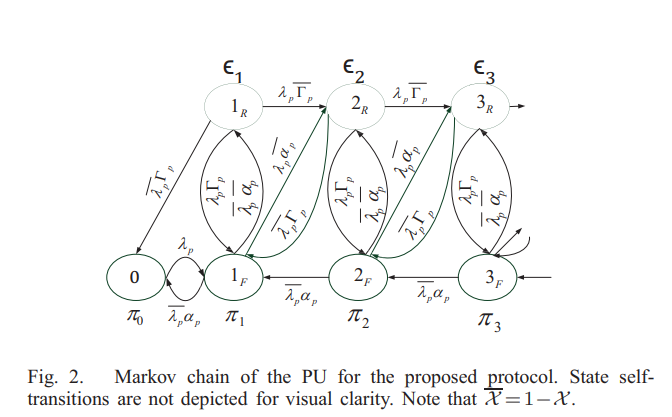
Maximum throughput of a secondary user cooperating with an energy-aware primary user
This paper proposes a cooperation protocol between a secondary user (SU) and a primary user (PU) which dedicates a free frequency subband for the SU if cooperation results in energy saving. Time is slotted and users are equipped with buffers. Under the proposed protocol, the PU releases portion of its bandwidth for secondary transmission. Moreover, it assigns a portion of the time slot duration for the SU to relay primary packets and achieve a higher successful packet reception probability at the primary receiver. We assume that the PU has three states: idle, forward, and retransmission states

Optimizing Cooperative Cognitive Radio Networks Performance with Primary QoS Provisioning
We consider the problem of optimizing the performance of a cooperative cognitive radio user subject to constraints on the quality-of-service (QoS) of the primary user (PU). In particular, we design the probabilistic admission control parameter of the PU packets in the secondary user (SU) relaying queue and the randomized service parameter at the SU under non-work-conserving (non-WC) and WC cooperation policies. In the non-WC policy, two constrained optimization problems are formulated; the first problem is maximizing the SU throughput while the second problem is minimizing the SU average delay
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 29
- Next page ››
