Breadcrumb
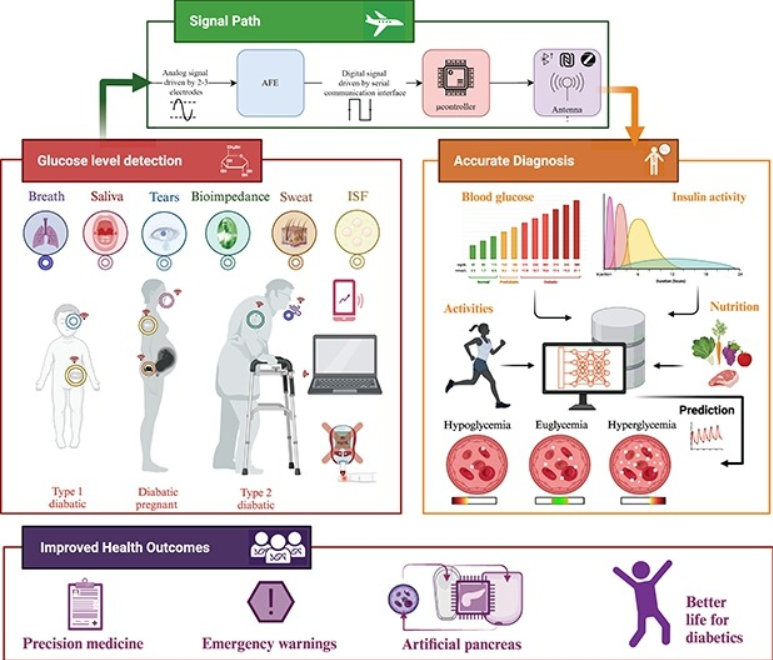
Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood glucose levels and can cause damage to multiple organs over time. Continuous monitoring of glucose levels is essential for both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals. There have been major developments in glucose monitoring technology over the past decade, which have been driven by research and industry efforts. Despite these significant advancements, the area of glucose biosensors still faces significant challenges. This paper presents a comprehensive summary of the latest glucose monitoring technologies, including invasive
Liver Disease Diagnosis using Tree-Based Machine Learning Algorithms
Liver Disease (LD) is a lethal yet relatively common disorder that is impacting the lives of millions across the world, causing slow yet irreversible internal organ damage or total organ failure if left untreated. In this study, LD is determined as the damage a Liver sustained due to excessive drug or alcohol abuse and other causes which leave severe scarring on the Liver leading to permanent functionality loss or cancer. This study revolves around determining if a person suffers from the disease regardless of the stage of the disease. To detect and minimize the impact of LD, tree-based
Developing an Ultra-Dense Optical Frequency Comb Using an Integrated MZM and SPM Schemes in HNLF
Optical frequency comb (OFC) is a broad spec-trum comprised of closely spaced equidistant narrow lines. The generation of OFC is based on several nonlinear effects in highly nonlinear fiber (HNLF), which is employed to produce the repetitive frequencies. This work investigates the usage of cascaded Mach-Zehnder modulators (MZM) and self-phase modulation (SPM) in HNLF as effective spectrum broadening and comb generation techniques. Several parameters have been investigated in order to improve the output spectrum of the comb generation system. The parameters being investigated in this research
Accelerated Edge Detection Algorithm for High-Speed Applications
Digital Image Processing (DIP) is a growing field for various applications, such as autonomous vehicles and video surveillance. To improve the performance of DIP systems, image processing algorithms are implemented in hardware rather than software. The idea here is primarily to get a faster system than software imaging or other alternative hardware. Field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) have the advantages of parallel processing, low cost, and low power consumption. These semiconductor devices contain many logic blocks that can be programmed to perform everything from basic digital gate-level

Relay Selection in NOMA-Based Cooperative Wireless Backhaul Networks
The joint application of wireless backhaul networks and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) hold the potential to fulfill the increasing demands of fifth-generation (5G) communication networks and beyond. It is usual in wireless backhaul networks to take assistance from small cell base stations acting as intermediate relays to reach the remote destination. This cooperative communication is an acknowledged technique to combat multi-path fading, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the reliability and capacity of wireless networks. This article studies the application of relay selection (RS)

An Intelligent Handwritten Digits and Characters Recognition System
The process of giving machines the ability to recognize human handwritten digits and characters is known as handwritten digit and character recognition. Handwritten digits and characters are imperfect, vary from person to person, and can be constructed with a variety of flavors. Therefore, it's not a simple assignment for the machine. In this paper, a machine learning algorithm has been made to detect handwritten digits and characters with high accuracy relative to the past models. The MNIST dataset is used to provide the model with the training and test datasets for its variety of data
A novel artificial intelligent-based approach for real time prediction of telecom customer’s coming interaction
Predicting customer’s behavior is one of the great challenges and obstacles for business nowadays. Companies take advantage of identifying these future behaviors to optimize business outcomes and create more powerful marketing strategies. This work presents a novel real-time framework that can predict the customer’s next interaction and the time of that interaction (when that interaction takes place). Furthermore, an extensive data exploratory analysis is performed to gain more insights from the data to identify the important features. Transactional data and static profile data are integrated
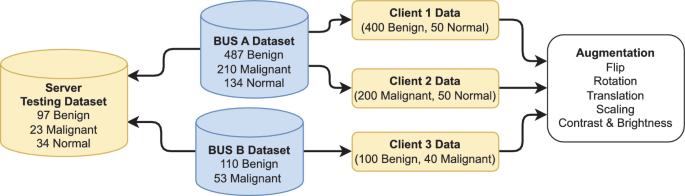
A Novel Approach to Breast Cancer Segmentation Using U-Net Model with Attention Mechanisms and FedProx
Breast cancer is a leading cause of death among women worldwide, emphasizing the need for early detection and accurate diagnosis. As such Ultrasound Imaging, a reliable and cost-effective tool, is used for this purpose, however the sensitive nature of medical data makes it challenging to develop accurate and private artificial intelligence models. A solution is Federated Learning as it is a promising technique for distributed machine learning on sensitive medical data while preserving patient privacy. However, training on non-Independent and non-Identically Distributed (non-IID) local datasets
Integrating Smart Contracts with WDNs Framework for Energy Management and Secure Transactions
The management of energy consumption and payment transactions using a secure, decentralized energy system framework is essential in the water distribution network (WDN). The water energy market, in which energy may be transformed into a digital asset that is potentially monitored, trackable and tradable, might greatly benefit from the deployment of blockchain technology. This is because the blockchain has transaction privacy, decentralization, security, and immutability features. Furthermore, using blockchain smart contracts enables energy market management operations such as consumers
SSHC with One Capacitor for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting
Piezoelectric vibration energy harvesters have attracted a lot of attention as a way to power self-sustaining electronic systems. Furthermore, as part of the growing Internet of Things (loT) paradigm, the ongoing push for downsizing and higher degrees of integration continues to constitute major drivers for autonomous sensor systems. Two of the most effective interface circuits for piezoelectric energy harvesters are synchronised switch harvesting (SSH) on inductor and synchronous electrical charge extraction; nevertheless, inductors are essential components in both interfaces. This study
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››
