Breadcrumb
Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends
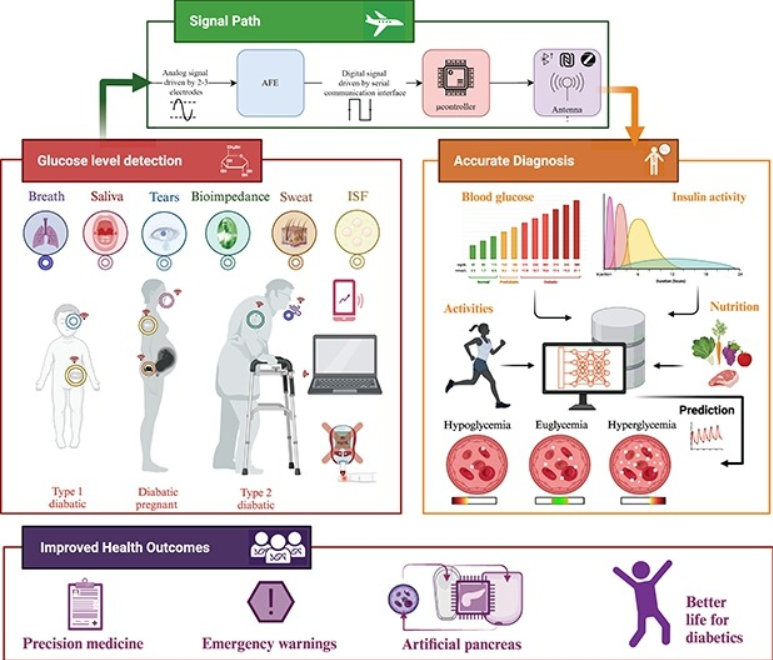
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood glucose levels and can cause damage to multiple organs over time. Continuous monitoring of glucose levels is essential for both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals. There have been major developments in glucose monitoring technology over the past decade, which have been driven by research and industry efforts. Despite these significant advancements, the area of glucose biosensors still faces significant challenges. This paper presents a comprehensive summary of the latest glucose monitoring technologies, including invasive
A novel artificial intelligent-based approach for real time prediction of telecom customer’s coming interaction
Predicting customer’s behavior is one of the great challenges and obstacles for business nowadays. Companies take advantage of identifying these future behaviors to optimize business outcomes and create more powerful marketing strategies. This work presents a novel real-time framework that can predict the customer’s next interaction and the time of that interaction (when that interaction takes place). Furthermore, an extensive data exploratory analysis is performed to gain more insights from the data to identify the important features. Transactional data and static profile data are integrated
Integrating Smart Contracts with WDNs Framework for Energy Management and Secure Transactions
The management of energy consumption and payment transactions using a secure, decentralized energy system framework is essential in the water distribution network (WDN). The water energy market, in which energy may be transformed into a digital asset that is potentially monitored, trackable and tradable, might greatly benefit from the deployment of blockchain technology. This is because the blockchain has transaction privacy, decentralization, security, and immutability features. Furthermore, using blockchain smart contracts enables energy market management operations such as consumers
SSHC with One Capacitor for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting
Piezoelectric vibration energy harvesters have attracted a lot of attention as a way to power self-sustaining electronic systems. Furthermore, as part of the growing Internet of Things (loT) paradigm, the ongoing push for downsizing and higher degrees of integration continues to constitute major drivers for autonomous sensor systems. Two of the most effective interface circuits for piezoelectric energy harvesters are synchronised switch harvesting (SSH) on inductor and synchronous electrical charge extraction; nevertheless, inductors are essential components in both interfaces. This study

Energy Aware Tikhonov-Regularized FPA Technique for Task Scheduling in Wearable Biomedical Devices
Harvesting the energy from environmental sources is a promising solution for perpetual and continuous operation of biomedical wearable devices. Although the energy harvesting technology ensures the availability of energy source, yet power management is crucial to ensure prolonged and stable operation under a stringent power budget. Thus, power-aware task scheduling can play a key role in minimizing energy consumption to improve system durability while maintaining device functionality. This chapter proposes a novel biosensor task scheduling of energy harvesting-based biomedical wearable devices

Sustainable Energy-Aware Task Scheduling for Wearable Medical Device Using Flower Pollination Algorithm
Power management and energy conservation are crucial for medical wearable devices that rely on energy harvesting. These devices operate under strict power budgets and require prolonged and stable operation. To achieve this, Energy-aware task scheduling is proposed as a solution to minimize energy consumption while ensuring the continued operational capabilities of the device. our paper presents a task scheduling method using the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA). The proposed task scheduling focuses on managing the activity of key components such as the heart rate sensor, temperature sensor

Improvement of piezoresistive pressure sensor using zig-zag shaped and PVDF material
Due to a wide range of applications in the biomedical industry, the need for flexible and wearable sensors is growing every day. A pressure sensor generates a signal based on the applied pressure. Sensors have become an integral component of our daily lives, from personal gadgets to industrial machinery. The identification of the low signal from the body necessitates the use of particularly sensitive sensors. The development of a pressure sensor that can transform the maximum input signal into an electrical output is critical. In this paper, zig-zag piezoresistors on a square diaphragm were
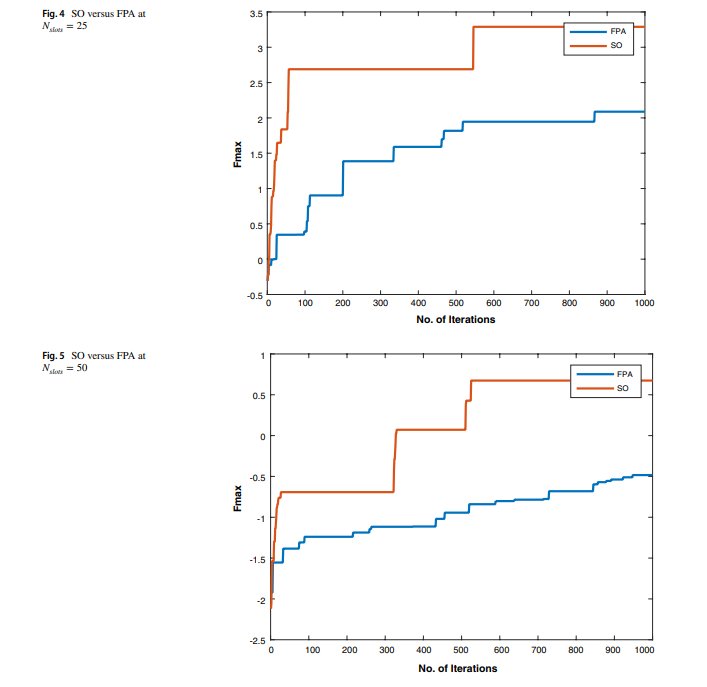
A power-aware task scheduler for energy harvesting-based wearable biomedical systems using snake optimizer
There is an increasing interest in energy harvesting for wearable biomedical devices. This requires power conservation and management to ensure long-term and steady operation. Hence, task scheduling algorithms will be used throughout this work to provide a reliable solution to minimize energy consumption while considering the system operation constraints. This study proposes a novel power-aware task scheduler to manage system operations. For example, we used the scheduler to handle system operations, including heart rate and temperature sensors. Two optimization techniques have been used to

Downlink Throughput Prediction in LTE Cellular Networks Using Time Series Forecasting
Long-Term Evolution (LTE) cellular networks have transformed the mobile business, as users increasingly require various network services such as video streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing. A network planning approach is required for network services to meet user expectations and meet their needs. The User DownLink (UE DL) throughput is considered the most effective Key Performance Indicator (KPI) for measuring the user experience. As a result, the forecast of UE DL throughput is essential in network dimensioning for the network planning team throughout the network design stage. The
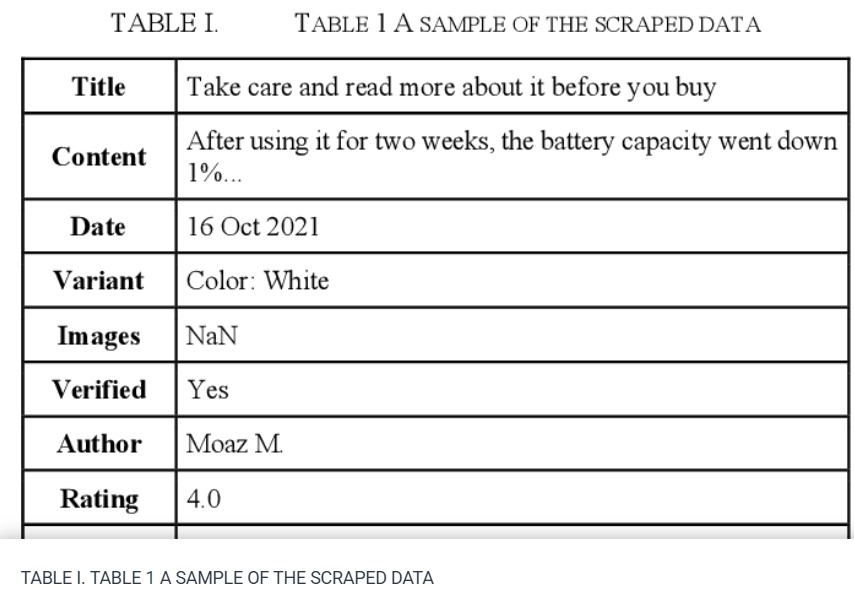
Sentiment Analysis: Amazon Electronics Reviews Using BERT and Textblob
The market needs a deeper and more comprehensive grasp of its insight, where the analytics world and methodologies such as 'Sentiment Analysis' come in. These methods can assist people especially 'business owners' in gaining live insights into their businesses and determining wheatear customers are satisfied or not. This paper plans to provide indicators by gathering real world Amazon reviews from Egyptian customers. By applying both Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers 'Bert' and 'Text Blob' sentiment analysis methods. The processes shall determine the overall satisfaction
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››
