Breadcrumb
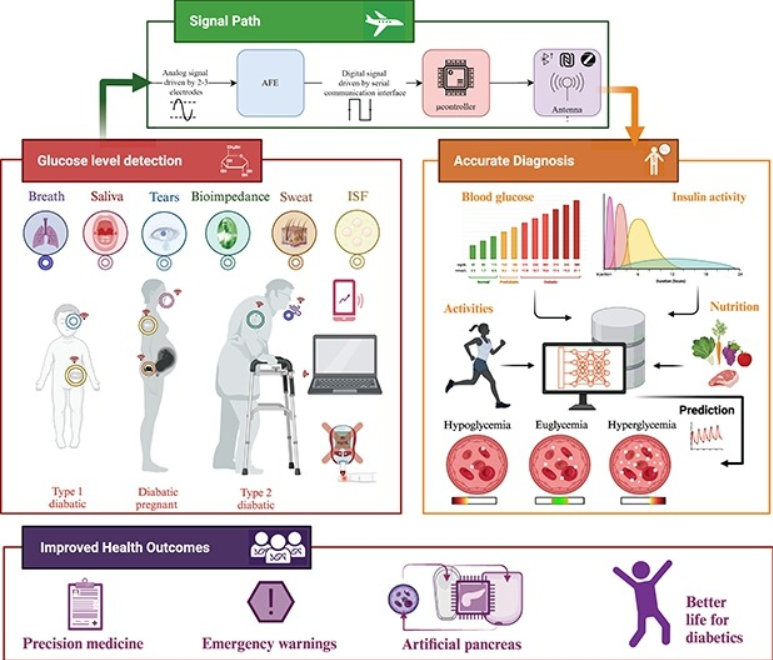
Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood glucose levels and can cause damage to multiple organs over time. Continuous monitoring of glucose levels is essential for both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals. There have been major developments in glucose monitoring technology over the past decade, which have been driven by research and industry efforts. Despite these significant advancements, the area of glucose biosensors still faces significant challenges. This paper presents a comprehensive summary of the latest glucose monitoring technologies, including invasive
Liver Disease Diagnosis using Tree-Based Machine Learning Algorithms
Liver Disease (LD) is a lethal yet relatively common disorder that is impacting the lives of millions across the world, causing slow yet irreversible internal organ damage or total organ failure if left untreated. In this study, LD is determined as the damage a Liver sustained due to excessive drug or alcohol abuse and other causes which leave severe scarring on the Liver leading to permanent functionality loss or cancer. This study revolves around determining if a person suffers from the disease regardless of the stage of the disease. To detect and minimize the impact of LD, tree-based
Developing an Ultra-Dense Optical Frequency Comb Using an Integrated MZM and SPM Schemes in HNLF
Optical frequency comb (OFC) is a broad spec-trum comprised of closely spaced equidistant narrow lines. The generation of OFC is based on several nonlinear effects in highly nonlinear fiber (HNLF), which is employed to produce the repetitive frequencies. This work investigates the usage of cascaded Mach-Zehnder modulators (MZM) and self-phase modulation (SPM) in HNLF as effective spectrum broadening and comb generation techniques. Several parameters have been investigated in order to improve the output spectrum of the comb generation system. The parameters being investigated in this research
Accelerated Edge Detection Algorithm for High-Speed Applications
Digital Image Processing (DIP) is a growing field for various applications, such as autonomous vehicles and video surveillance. To improve the performance of DIP systems, image processing algorithms are implemented in hardware rather than software. The idea here is primarily to get a faster system than software imaging or other alternative hardware. Field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) have the advantages of parallel processing, low cost, and low power consumption. These semiconductor devices contain many logic blocks that can be programmed to perform everything from basic digital gate-level

Relay Selection in NOMA-Based Cooperative Wireless Backhaul Networks
The joint application of wireless backhaul networks and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) hold the potential to fulfill the increasing demands of fifth-generation (5G) communication networks and beyond. It is usual in wireless backhaul networks to take assistance from small cell base stations acting as intermediate relays to reach the remote destination. This cooperative communication is an acknowledged technique to combat multi-path fading, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the reliability and capacity of wireless networks. This article studies the application of relay selection (RS)
Automatic Detection of Alzheimer Disease from 3D MRI Images using Deep CNNs
Alzheimer's disease (AD), also referred to simply as Alzheimer's, is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and worsens over time. It is the cause of 60% to 70% of cases of dementia. In 2015, there were approximately 29.8 million people worldwide with AD. It most often begins in people over 65 years of age as it affects about 6% of people 65 years and older, although 4% to 5% of cases are early-onset Alzheimer's which begin before this. In 2015, researchers have figured out that dementia resulted in about 1.9 million deaths. Continuous efforts are made to cure the
Cooperative MEC With Non-Uniform User Density: Resource Planning and State Control Optimization
Mobile edge computing (MEC) allows mobile devices to offload computationally intensive tasks to nearby base stations equipped with computational resources. MEC also provides a solution for supporting low latency responses. However, MEC increases the system power consumption by adding extra computational units. It is important to carefully plan computational resources to achieve a balance between quality of service (QoS) and power consumption. Moreover, the MEC system control should shut down unused resources when traffic rates fall to further decrease the power consumption. In this letter, we

An Optimized Non-Invasive Blood Glucose and Temperature Body Measurement System
Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not adequately process food for energy production. Most of the food we consume is converted into glucose, or sugar, which our bodies use for energy. Moreover, the pancreas, which is an organ located near the stomach, produces insulin, a hormone that aids in the transport of glucose into our bodies' cells. Diabetes occurs when your body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use its own insulin the way it is supposed to. Sugars accumulate in your blood as a result of this. This is why diabetes is often referred to as "sugar". People with
Cross-Junction Based Metasurface for Wideband 90° Polarization Rotation
In this work, an ultrathin subwavelength metasurface based on a cross-junction-inspired unit cell that exhibits efficient wideband polarization rotation is presented. This structure manipulates the polarization of the incident electromagnetic radiation in the transmission band. The proposed metasurface converts the incident linearly polarized waves into the orthogonal polarization over a fractional bandwidth of 9.6% with a maximum insertion loss of 0.65 dB. The detailed analysis of the structure's inherent resonances and their origins are also presented with special emphasis on the intrinsic

An Intelligent Handwritten Digits and Characters Recognition System
The process of giving machines the ability to recognize human handwritten digits and characters is known as handwritten digit and character recognition. Handwritten digits and characters are imperfect, vary from person to person, and can be constructed with a variety of flavors. Therefore, it's not a simple assignment for the machine. In this paper, a machine learning algorithm has been made to detect handwritten digits and characters with high accuracy relative to the past models. The MNIST dataset is used to provide the model with the training and test datasets for its variety of data
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››
