Breadcrumb
Towards Intelligent Web Context-Based Content On-Demand Extraction Using Deep Learning
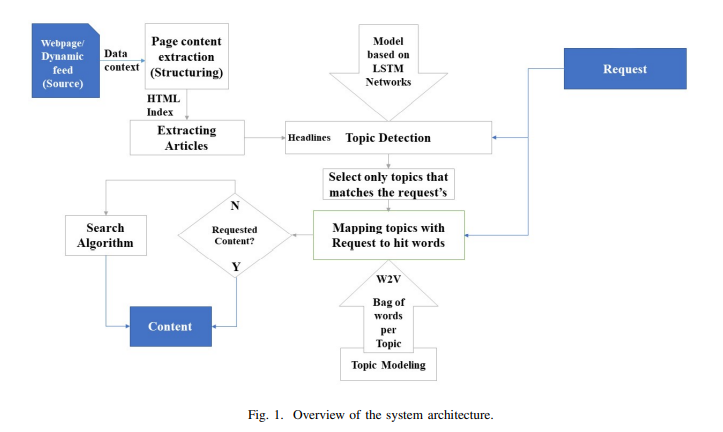
Information extraction and reasoning from massive high-dimensional data at dynamic contexts, is very demanding and yet is very hard to obtain in real-time basis. However, such process capability and efficiency might be affected and limited by the available computational resources and the consequent power consumption. Conventional search mechanisms are often incapable of real-time fetching a predefined content from data source, without concerning the increased number of connected devices that contribute to the same source. In this work, we propose and present a concept for an efficient approach
Optimum Scheduling of the Disinfection Process for COVID-19 in Public Places with a Case Study from Egypt, a Novel Discrete Binary Gaining-Sharing Knowledge-Based Metaheuristic Algorithm
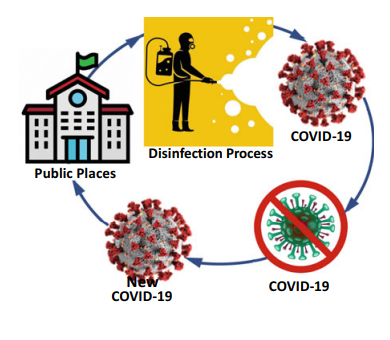
The aim of this paper is to introduce an improved strategy for controlling COVID-19 and other pandemic episodes as an environmental disinfection culture for public places. The scheduling aims at achieving the best utilization of the available working day-time hours, which is calculated as the total consumed disinfection times minus the total loosed transportation times. The proposed problem in network optimization identifies a disinfection group who is likely to select a route to reach a subset of predetermined public places to be regularly disinfected with the most utilization of the
Alternate relaying and the degrees of freedom of one-way cellular relay networks
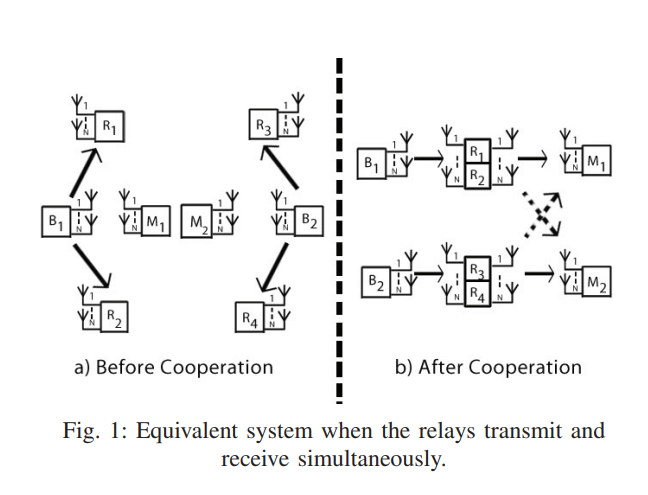
In this paper, a cellular relaying network consisting of two source-destination pairs, and four decode-and-forward relays operating in half-duplex mode is considered. Each source is assisted by two relays and all nodes are equipped with N antennas. In order to compensate for the loss of capacity by a factor of half due to the half-duplex mode, an alternate transmission protocol among the two relays is proposed. An outer bound on the degrees of freedom (DoF) of this system is developed. A constructive proof of achievability based on two different schemes is provided. Aligning the inter-relay
An achievable rate region for a primary network shared by a secondary link
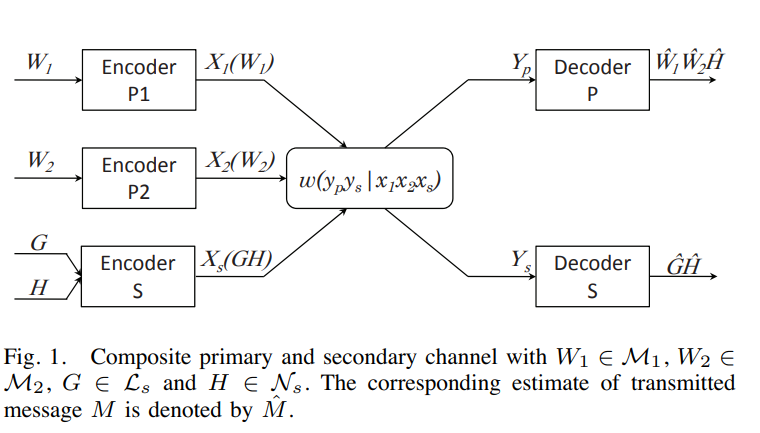
We consider a multiple access primary network with N transmitters. A secondary link of one transmitter and a corresponding receiver causes interference to the primary network. An achievable rate region for the primary network and the secondary link is obtained given the following mode of operation. The secondary transmitter employs rate-splitting so that the primary receiver can decode part of the secondary's signal and cancel it. The secondary receiver, on the other hand, treats primary interference as noise. Given a Gaussian channel model, we investigate the effect of rate-splitting on the
Alternate versus simultaneous relaying in MIMO cellular relay networks: A degrees of freedom study
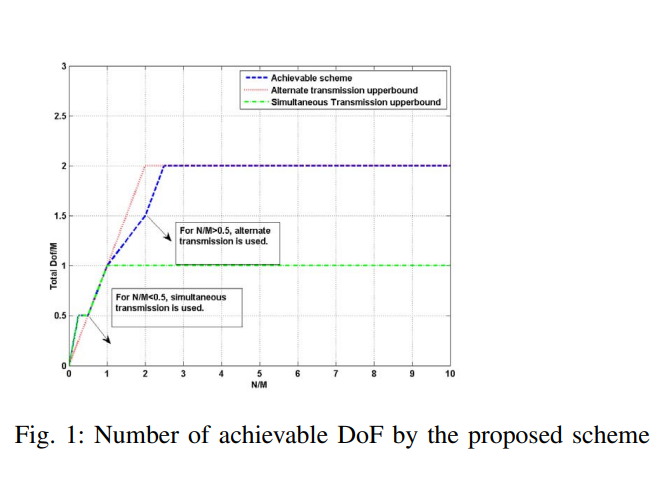
In this paper, a two-hop cellular relay network consisting of two source-destination pairs equipped with M antennas is considered where each source is assisted by two decode-and-forward relays operating in half-duplex mode and the relays are equipped with N antennas. The DoF of the system is investigated for both simultaneous and alternate relaying configurations. For each relay configuration, an outer bound on the degrees of freedom (DoF) is developed. A new achievable scheme is proposed that meets the upper bound on the maximum DoF for all values of M andN except for M
A degrees of freedom-optimal scheme for SISO X channel with synergistic alternating CSIT
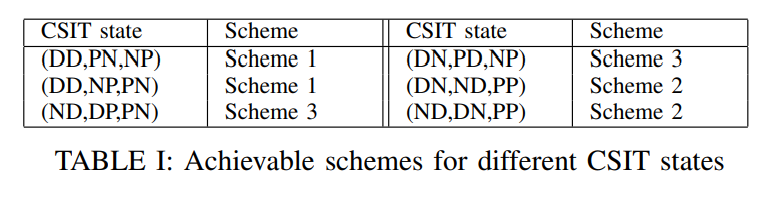
In this paper, the degrees of freedom (DoF) of the two-user single input single output (SISO) X channel are investigated. Three cases are considered for the availability of channel state information at the transmitters (CSIT); perfect, delayed, and no-CSIT. A new achievable scheme is proposed to elucidate the potency of interference creation-resurrection (IRC) when the available CSIT alternates between these three cases. For some patterns of alternating CSIT, the proposed scheme achieves 4/3 DoF, and hence, coincides with the information theoretic upper bound on the DoF of the X channel with
Distributed admission and power control for cognitive radios in spectrum underlay networks
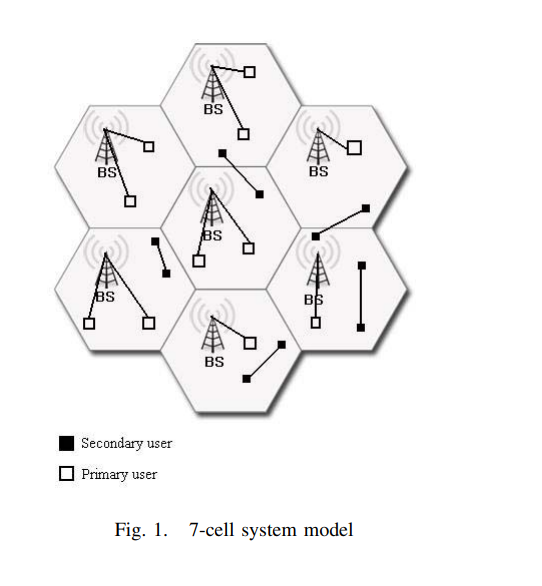
In this paper we investigate admission control and power allocation for cognitive radios in an underlay network. We consider the problem of maximizing the number of supported secondary links under their minimum QoS requirements without violating the maximum tolerable interference on primary receivers in a cellular network. An optimal solution to our problem is shown in previous works to be NP-hard. We propose an efficient distributed algorithm with reasonable complexity that provides results close to the optimum solution without requiring neither a large amount of signaling nor a wide range of
Towards energy efficient relay placement and load balancing in future wireless networks
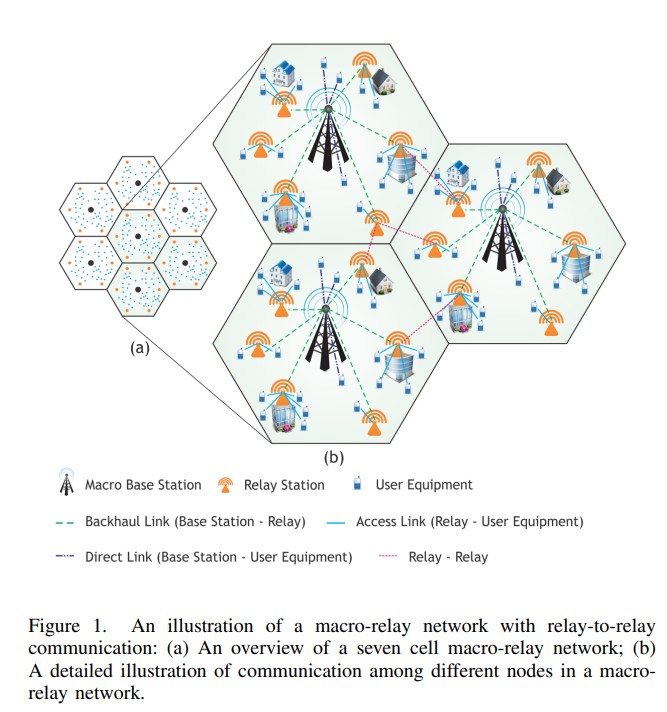
This paper presents an energy efficient relay deployment algorithm that determines the optimal location and number of relays for future wireless networks, including Long Term Evolution (LTE)-Advanced heterogeneous networks. We formulate an energy minimization problem for macro-relay heterogeneous networks as a Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) problem. The proposed algorithm not only optimally connects users to either relays or eNodeBs (eNBs), but also allows eNBs to switch into inactive mode. This is possible by enabling relay-to-relay communication which forms the basis for relays to
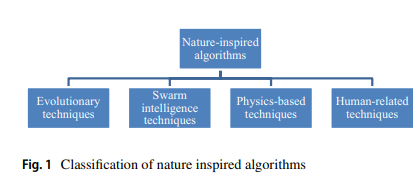
Gaining-sharing knowledge based algorithm for solving optimization problems: a novel nature-inspired algorithm
This paper proposes a novel nature-inspired algorithm called Gaining Sharing Knowledge based Algorithm (GSK) for solving optimization problems over continuous space. The GSK algorithm mimics the process of gaining and sharing knowledge during the human life span. It is based on two vital stages, junior gaining and sharing phase and senior gaining and sharing phase. The present work mathematically models these two phases to achieve the process of optimization. In order to verify and analyze the performance of GSK, numerical experiments on a set of 30 test problems from the CEC2017 benchmark for
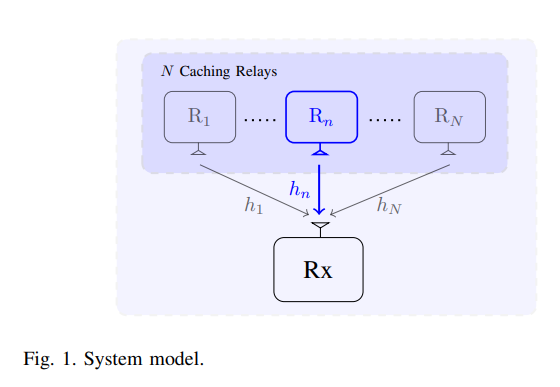
Proactive power allocation and caching node selection for regular service guarantees
This paper studies the potential of proactive resource allocation to prolong the communication sessions in networks with limited energy budgets and stringent quality-of-service (QoS) requirement, particularly a regular service guarantee. A threshold-based proactive communication policy is proposed to minimize the consumed transmission energy and maximize the network lifetime based on the different link states and the buffer state at the destination node. A closed-form expression is presented for the proactive gain in terms of the channel gain threshold, the amount of the proactively-
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››

