Breadcrumb
Fingerprinting with minimum distance decoding
This paper adopts an information-theoretic framework for the design of collusion-resistant coding/decoding schemes for digital fingerprinting. More specifically, the minimum distance decision rule is used to identify 1 out of $t$ pirates. Achievable rates, under this detection rule, are characterized in two scenarios. First, we consider the averaging attack where a random coding argument is used to show that the rate 1/2 is achievable with $t=2$ pirates. Our study is then extended to the general case of arbitrary $t$ highlighting the underlying complexity-performance tradeoff. Overall, these
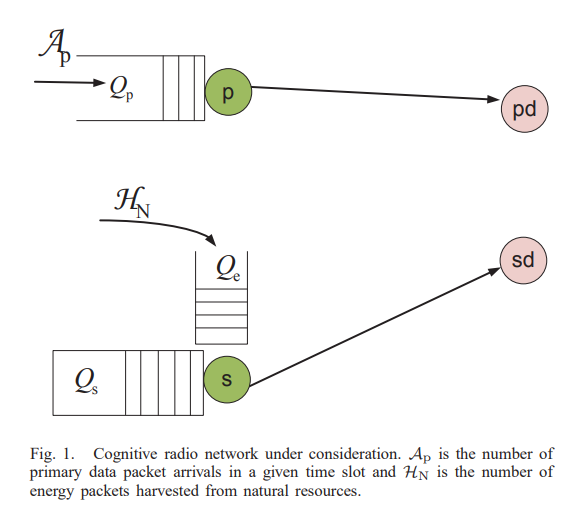
Optimal spectrum access for a rechargeable cognitive radio user based on energy buffer state
This paper investigates the maximum throughput for a rechargeable secondary user (SU) sharing the spectrum with a primary user (PU) plugged to a reliable power supply. The SU maintains a finite energy queue and harvests energy from natural resources, e.g., solar, wind and acoustic noise. We propose a probabilistic access strategy by the SU based on the number of packets at its energy queue. In particular, when the energy queue is in a certain state, the SU probabilistically uses a total number of energy packets that is at most equal to the number of packets at its energy queue. The probability
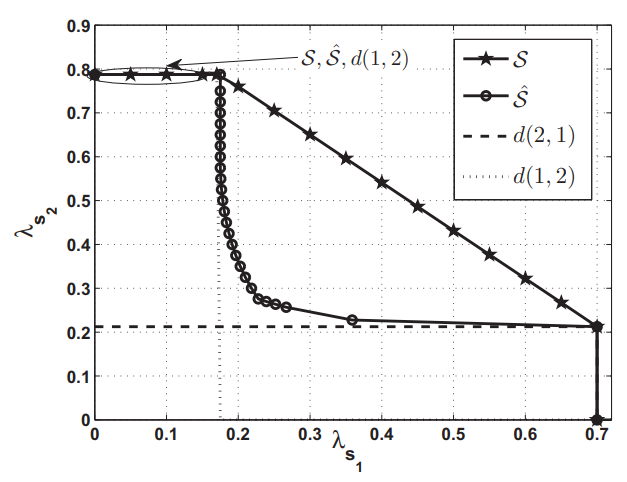
Band allocation for cognitive radios with buffered primary and secondary users
In this paper, we study band allocation of Ms buffered secondary users (SUs) to Mp orthogonal primary licensed bands, where each primary band is assigned to one primary user (PU). Each SU is assigned to one of the available primary bands with a certain probability designed to satisfy some specified quality of service (QoS) requirements for the SUs. In the proposed system, only one SU is assigned to a particular band. The optimization problem used to obtain the stability region's envelope (closure) is shown to be a linear program. We compare the stability region of the proposed system with that
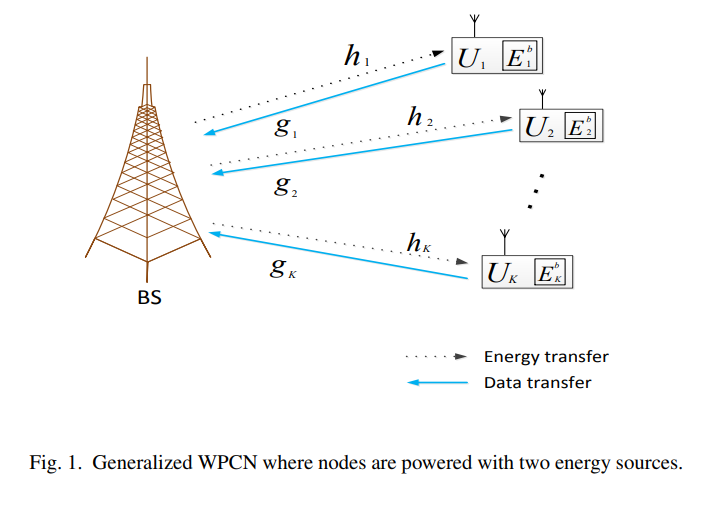
Optimization of energy-constrained wireless powered communication networks with heterogeneous nodes
In this paper, we generalize conventional time division multiple access (TDMA) wireless networks to a new type of wireless networks coined generalized wireless powered communication networks (g-WPCNs). Our prime objective is to optimize the design of g-WPCNs where nodes are equipped with radio frequency (RF) energy harvesting circuitries along with constant energy supplies. This constitutes an important step towards a generalized optimization framework for more realistic systems, beyond prior studies where nodes are solely powered by the inherently limited RF energy harvesting. Towards this
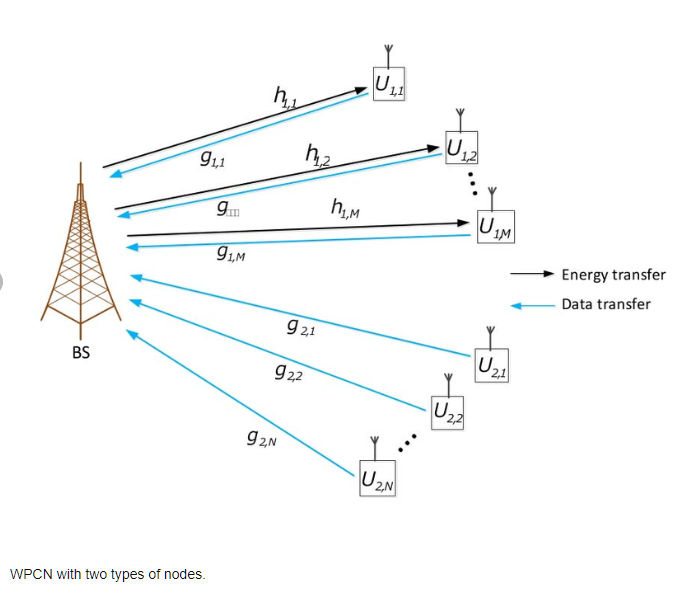
Optimization of wireless powered communication networks with heterogeneous nodes
This paper studies optimal resource allocation in a wireless powered communication network with two groups of users; one is assumed to have radio frequency (RF) energy harvesting capability and no other energy sources, while the other group has legacy nodes that are assumed not to have RF energy harvesting capability and are equipped with dedicated energy supplies. First, the base-station (BS) with a constant power supply broadcasts an energizing signal over the downlink. Afterwards, all users transmit their data independently on the uplink using time division multiple access (TDMA). We
Cooperative D2D communications in the uplink of cellular networks with time and power division
Cooperative device-to-device (D2D) communication is proposed as a promising technology to improve the spectral efficiency in crowded communication networks. In this paper, we consider a transmitter-receiver pair, operating in the D2D transmission mode, overlaying the cellular network. The D2D transmitter (DT) acts as a relay for the undelivered packets of cellular user equipment (CUE). We consider the case in which the DT transmits its own data along with the relayed data using superposition coding in the uplink. We investigate how the time slot is split between the cellular network
Resource allocation for throughput enhancement in cellular shared relay networks
The downlink frame of a cellular relay network is considered, where a shared MIMO decode-and-froward relaying is used to serve the users at the edge of the cell. The relay employs zero-forcing beamforming to manage the interference among the mobile stations (MSs) at the edge of the cell. A non-cooperative scheme is considered where there is no coordination between the base stations (BSs) and the relay station (RS), and a power control algorithm for the RS is developed that maximizes the rate of the relayed users. A cooperative setting which allows the coordination of a power allocation between
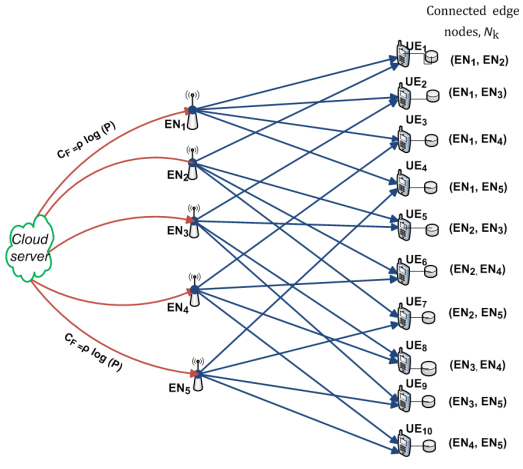
Cache-Aided Combination Networks with Interference
Centralized coded caching and delivery is studied for a radio access combination network (RACN), whereby a set of H edge nodes (ENs), connected to a cloud server via orthogonal fronthaul links with limited capacity, serve a total of K user equipments (UEs) over wireless links. The cloud server is assumed to hold a library of N files, each of size F bits; and each user, equipped with a cache of size μ R N F bits, is connected to a distinct set of r ENs each of which equipped with a cache of size μTNF bits, where μT , μ R in [{0,1}] are the fractional cache capacities of the UEs and the ENs
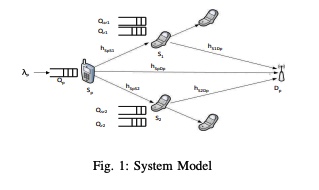
A dynamic relaying scheme for cognitive networks with multipacket reception capability
We study a cognitive radio system where the secondary users can relay the unsuccessful packets of the primary user. We study a model with one primary link and two secondary links with Multipacket Reception capability (MPR) added to the receivers. Secondary users relaying the primary unsuccessful packets are shown to increase the primary maximum stable throughput and increase the secondary user transmission opportunities. MPR capability is shown to further increase the secondary transmission opportunities as the secondary users can relay with a rate higher than 1 packets/slot as opposed to

Optimal selection of spectrum sensing duration for an energy harvesting cognitive radio
In this paper, we consider a time-slotted cognitive radio (CR) setting with buffered and energy harvesting primary and CR users. At the beginning of each time slot, the CR user probabilistically chooses the spectrum sensing duration from a predefined set. If the primary user (PU) is sensed to be inactive, the CR user accesses the channel immediately. The CR user optimizes the sensing duration probabilities in order to maximize its mean data service rate with constraints on the stability of the primary and cognitive queues. The optimization problem is split into two subproblems. The first is a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 23
- Next page ››
