Breadcrumb

Downlink Throughput Prediction in LTE Cellular Networks Using Time Series Forecasting
Long-Term Evolution (LTE) cellular networks have transformed the mobile business, as users increasingly require various network services such as video streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing. A network planning approach is required for network services to meet user expectations and meet their needs. The User DownLink (UE DL) throughput is considered the most effective Key Performance Indicator (KPI) for measuring the user experience. As a result, the forecast of UE DL throughput is essential in network dimensioning for the network planning team throughout the network design stage. The
Light-Weight Face Shape Classifier for Real-Time Applications
Deep neural networks (DNNs) are memory and computationally intensive; hence they are difficult to apply to real-time systems with limited resources. Therefore, the DNN models need to be carefully optimized. The solution was a model based on a convolutional neural network (CNN) called MobileNet that decreases the computational and space complexities with classification precision loss by utilizing depthwise separable convolutions. This study uses MobileNet vl architecture to improve image classification complexities to reach an acceptable complexity that can be used in real-time applications
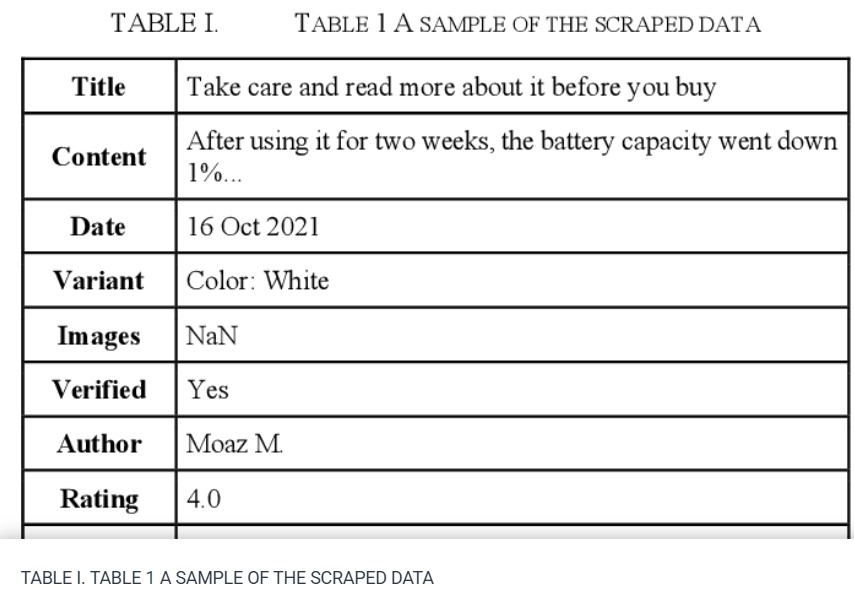
Sentiment Analysis: Amazon Electronics Reviews Using BERT and Textblob
The market needs a deeper and more comprehensive grasp of its insight, where the analytics world and methodologies such as 'Sentiment Analysis' come in. These methods can assist people especially 'business owners' in gaining live insights into their businesses and determining wheatear customers are satisfied or not. This paper plans to provide indicators by gathering real world Amazon reviews from Egyptian customers. By applying both Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers 'Bert' and 'Text Blob' sentiment analysis methods. The processes shall determine the overall satisfaction
A Generic AI-Based Technique for Assessing Student Performance in Conducting Online Virtual and Remote Controlled Laboratories
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the development of educational technology, e-learning has become essential in the educational process. However, the adoption of e-learning in sectors such as engineering, science, and technology faces a particular challenge as it needs a special Laboratory Learning Management System (LLMS) capable of supporting online lab activities through virtual and controlled remote labs. One of the most challenging tasks in designing such LLMS is how to assess a student's performance while an experiment is being conducted and how stuttering students can be automatically

Integrated Trust-Clustering and Dijkstra Routing Algorithms for Energy-Efficient WSNs
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) playa crucial role in various fields but are highly susceptible to external attacks, making the development of secure data aggregation methods in WSNs imperative. To enhance the security of WSNs, this study introduces a Trust-Based Clustering and Dijkstra-Based Routing algorithm (TBC-DBR). The proposed algorithm aims to establish a secure and efficient data aggregation mechanism in WSNs. It begins by dividing the sensor nodes into clusters, creating a structured network architecture. Within each cluster, the members undergo a three-phase trust evaluation process

Stability Analysis and Fault Detection of Telecommunication Towers Using Decision Tree Algorithm under Wind Speed Condition
This paper presents a decision tree (DT) modeling technique to estimate any increase in the load on telecommunication towers. A structural analysis was done for the lattice and mono-pole towers using TNX Tower software to determine the basic features of the towers, such as tilt angle, deflection, twist, and acceleration. The structure analysis generated a data set based on wind speeds. This data set was then used to train a machine-learning algorithm to estimate the loads on the structure. Any change in the applied loads greater than the loads considered in the design might be identified using

Indoor Air Quality Monitoring Systems for Sustainable Medical Rooms and Enhanced Life Quality
Indoor air pollution poses a substantial risk to human health and well-being, underscoring the crucial requirement for efficient monitoring systems. This paper introduces an advanced Air Pollution Monitoring System (APMS) tailored explicitly for indoor settings. The APMS integrates sensors and a user interface, ensuring the delivery of real-time and precise data concerning air quality parameters such as particulate matter (PM), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon dioxide (CO2), as well as temperature and humidity. The proposed APMS has several advantages, including low maintenance
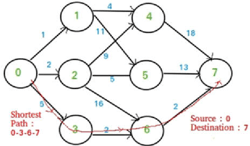
Comparison of Parallel and Serial Execution of Shortest Path Algorithms
Shortest Path Algorithms are an important set of algorithms in today's world. It has many applications like Traffic Consultation, Route Finding, and Network Design. It is essential for these applications to be fast and efficient as they mostly require real-Time execution. Sequential execution of shortest path algorithms for large graphs with many nodes is time-consuming. On the other hand, parallel execution can make these applications faster. In this paper, three popular shortest path algorithms-Dijkstra, Bellman-Ford, and Floyd Warshall-Are both implemented as serial and parallel programs
Correction to: Optimization of energy-constrained wireless powered communication networks with heterogeneous nodes (Wireless Networks, (2019), 10.1007/s11276-017-1587-x)
The original version of this article contained error in author affiliation. Also, the article note and acknowledgement sections are missing. © 2018, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Light-Weight Intelligent Egyptian Food Detector For Diabetes Management
Diabetic patients need a management tool that combines multiple features and tracks and views detailed data time-efficiently. Effective food logging is an important element of health monitoring. In this paper, we propose 'Suger.ly', a lightweight mobile application with artificial intelligence food recognition for diabetes management. The system has been trained to recognize 101 distinct types of food, with a focus on Egyptian cuisine. The app can then get nutritional value and insulin calculations. The results obtained from the Single-Shot multibox Detection (SSD) MobileNet-V1 food detection
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 3
- Next page ››
